ヒルベルトの関係と最小位相
─周波数特性から最小位相特性を求める例─
周波数特性の絶対値がわかっているときに、ヒルベルトの関係とFFTを使って最小位相を求めてみよう。
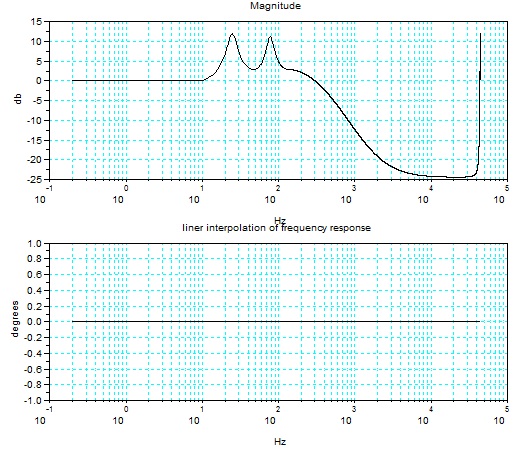
仮に、分析用の周波数特性のデータとして、周波数とその振幅についてのポイントデータがあるとする。ある周波数のポイントのデータがあるだけで、DCからサンプリング周波数までリニアにすべてのデータはないケースを考えてみよう。
FFT変換や 又、あとでインパルス応答を求めるのに便利なように、サンプリング周波数に分割した(つまり、時間上では1サンプル間隔が周波数上では1Hzに相当するように)周波数応答を ポイント間の直線補間で近似的に求めてみよう。
下記の図は、サンプリング周波数44.1KHzのときに、477個のポイントデータを直線補間して44100個のリニアなデータにして プロットしたもの
である。周波数特性の振幅の絶対値しかわからないので、位相特性(degrees)はゼロとなっている。右端の針のような線は、周波数を対数尺度で表示し
たためのもので、特性はサンプリング周波数の2分の1を中心に対称な値になっている。
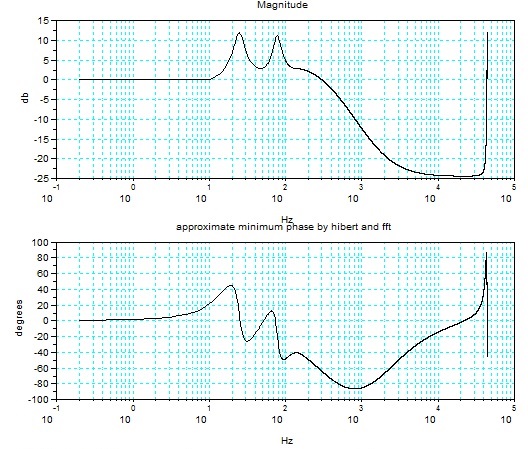
下図はヒルベルトの関係とFFTを使って、上図の周波数の振幅特性から最小位相(下段の位相特性)を求めたもの。離散的な変換を使っているので、ここでの値は最小位相の近似値となっている。FFTのポイント数を上げて、近似がよくなることを期待している。
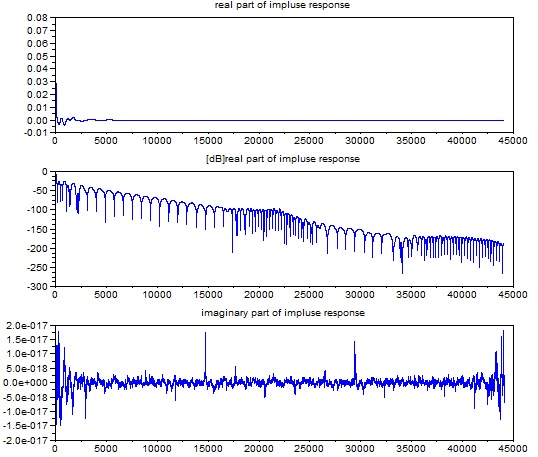
下図は、もとめた最小位相をもつ複素数の周波数特性をFFTで時間軸の値に変換して、インパルス応答?の信号に変換したものである。FFTした結果は、本来 複素数であるが、虚数部分は3段目の図のように(10のマイナス17乗のオーダーであり)ほぼゼロとみなすことができ、この
世?で実現可能な実数部だけのフィルターになっていることがわかる。2段目の図は、普通の振幅表示だと値が小さすぎてわかりずらいので、実部の絶対値を一番頭
の値を基準にdB(10のLOGして20倍)表示したものである。
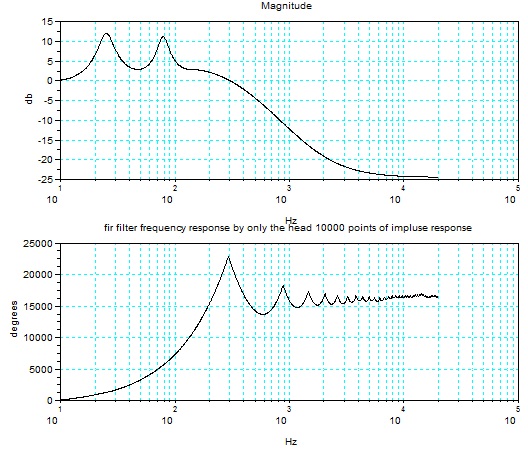
インパルス応答の先頭データが何個あれば もとの周波数特性が再現できるかを見たもので、下図は先頭から10000個のデータからなるFIRフィルターの周波数応答である。 例えば、データ数が4096個と少ないと、50Hz以下の周波数特性を上手く再現できない。
参考までに、この最小位相を計算するpythonプログラムをおいておきます。 これは、以前scilabで作成した下記のものをPythonで作り直したものです。 使い方は解凍した中にあるREADME.txtを見てください。
この周波数特性の絶対値から最小位相を求めるために使った
数値演算ライブラリ
SCILAB用のサンプルプログラムを参考までに以下に紹介します。 ここで使った周波数(f_data1.sci)とその振幅特性(H_data1.sci)のポイントデータはこちら。 このサンプルプログラムの動作保証はありませんのであしからず。
python
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// a study of hilbert transfer by scilab-4.1.2
//
// ..............................................................................
// WARNING: This program may have some bugs and you may modify this program.
// Everything done by your own risk, if you use this program.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//(1) read point data
disp('load data...');
exec("f_data1.sci"); // frequecny list, 1 means fs/2, half of sampling frequecny
exec("H_data1.sci"); // gain list
//
fs=44100.0; // sampling frequency
s0=size(f);
fscale0=0.5;
//--------------------------------------------------------
//(2) liner interpolation of frequency response
//
function [outf]=liner_inter(k0,xf)
k1=k0+1;
if k0== 0 then
db0= 1.0; // WARNING! Start point is always set to 1.0. 振幅のDC成分つまり一番はじめを1と仮定してある!
db1= H(k1);
fx0= 0.0;
fx1= f(k1) * fscale0;
else
db0= H(k0);
db1= H(k1);
fx0= f(k0) * fscale0;
fx1= f(k1) * fscale0;
end
outf= ( (db1 - db0) / (fx1 - fx0 )) * (xf - fx0 ) + db0;
endfunction
//
//--------------------------------------------------------
//(3) change point data to linear data
//
size_of_fft=int(fs); // Because to require impluse response by dft, size becomes as fs
dummy=0.00001; // minimum value, this needs log(ln)
freq_step= 1.0 / size_of_fft;
disp(freq_step*fs,'freq_step= ', );
freq_list=0:freq_step:(1-freq_step);
fl0=size(freq_list);
H_list=zeros(fl0(2),1);
sp0=1;
for k=1:fl0(2)
// DC :WARNING! Start point is always set to 1.0.
if k == 1 then
H_list(k)=liner_inter(0, 0.0);
// freq > 0.5 is Zero
elseif freq_list(k) > 0.5 then
H_list(k)=dummy;
// freq > f(end)
elseif freq_list(k) > (f(s0(1)) * fscale0) then
H_list(k)=dummy; // LOGをとったときにエラーにならないように 仮の小さい値を入れてある!
// freq < f(1)
elseif freq_list(k) < (f(1) * fscale0) then
H_list(k)=liner_inter(0, freq_list(k));
//
else
for v=sp0:(s0(1)-1)
if (freq_list(k) >= (f(v) * fscale0)) & (freq_list(k) <= (f(v+1) * fscale0)) then
H_list(k)=liner_inter(v, freq_list(k));
sp0=v;
break;
end
end
end
end
//----------------------------------
//(4) Copy alias image to upper half side
//
n0=length(H_list);
c0=2;
for k=n0:-1:(n0/2+1)
H_list(k) = H_list(c0);
c0=c0+1;
end
//----------------------------------
// (5) hilbert transfer by FFT
// H(z)=ln(|H(z)|) + j arg(H(z))
//
lnH_list=log(H_list); // ln(|H(input)|)
// More long n0, approximation of minimum phase will be good.
n0=length(lnH_list);
// h(n) is like hilbert filter
// h(n) is un(n) defined in Oppenheim & Schafer, Digital Signal Processing, page 19 (下)
h=zeros(lnH_list);
h(1)=1; // h(1)=1
if modulo(n0,2)==0 then
h(n0/2+1)=1;
h(2:n0/2)=2;
else
h(2:(n0+1)/2)=2;
end;
IFFT0=fft(lnH_list,1); //dft(lnH_list,1);
FFT0=fft(IFFT0 .* h,-1); // dft(IFFT0 .* h,-1);
// imag(FFT0) is approximate minimum phase
ComplexH_list=zeros(H_list);
for i=1:n0
ComplexH_list(i)= H_list(i) * exp( %i * imag(FFT0(i)));
end
//----------------------------------
// (6) require impluse response by FFT
//--------------------------------------------------
IRESP0=fft(ComplexH_list,1); // complex impluse response // dft(ComplexH_list,1);
IRESP0R=real(IRESP0); // get real part only
//--------------------------------------------------------
// (0) misc function for display
start_freq=10.0;
end_freq=20000.0;
step_freq=1000.0; // many is good
scale_mode=1; // 0 linear, 1 log
function [freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs()
//
mode0=scale_mode;
if end_freq > (1.1 * (fs/2.0)) then
end_freq= 0.9 * (fs/2.0);
end
if mode0==0 then // linear scale
step_freq=(end_freq-start_freq)/step_freq;
freqa=(start_freq:step_freq:end_freq);
freqd=((start_freq/fs):(step_freq/fs):(end_freq/fs));
end
if mode0==1 then // log scale
step0= (log(end_freq) - log(start_freq)) / step_freq;
bairitu0= exp( step0 );
freqa=zeros(1,2);
freqd=zeros(1,2);
freqa(1)=start_freq;
freqd(1)=freqa(1)/fs;
for v=1:int(step_freq)
freqa(v+1)=freqa(v) * bairitu0;
freqd(v+1)=freqa(v)/fs;
end
end
s0=size(freqa);
kosuu=s0(1,2);
endfunction
//--------------------------------------------------------
//(7) Output display
//
wb0=xget('window'); // stack old window
xset('window',0); // create new windows
clf();
fhz = freq_list * fs;
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(H_list);
//gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
fhz(1)=0.2; // WARNING: this escape bode freq 1st zero
bode(fhz, db0,phi0);
xtitle('liner interpolation of frequency response');
xset('window',1); // create new windows
clf();
fhz = freq_list * fs;
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(ComplexH_list);
//gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
fhz(1)=0.2; // WARNING: this escape bode freq 1st zero
bode(fhz, db0,phi0);
xtitle('approximate minimum phase by hibert and fft');
xset('window',2); // create new windows
clf();
subplot(311);
plot(real(IRESP0));
xtitle('real part of impluse response');
subplot(312);
plot(20.0 * log10( abs(real(IRESP0) / real(IRESP0(1)))));
xtitle('[dB]real part of impluse response');
subplot(313);
plot(imag(IRESP0));
xtitle('imaginary part of impluse response');
//------------------------------------------
// How long need of impluse response length enough ?
SampleL=4096; // 4096 is not enough
SampleL=10000; // 10000 is good
xIc=zeros(SampleL,1);
for i=1:SampleL
xIc(SampleL - i + 1)= real(IRESP0(i));
end
bunsi2=poly(xIc,'z','coeff');
xHi=syslin('d',bunsi2,1);
xset('window',3); // create new windows
clf();
[freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs();
[frq0, repf0]=repfreq(xHi,freqd);
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(repf0);
//gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
bode(freqa, db0,phi0);
xtitle('fir filter frequency response by only the head 10000 points of impluse response');
xset('window',wb0);
さて、周波数特性が与えられたときに、その特性を近似的に実現するIIRフィルターを求めることを考えてみよう。
残念ながら、今回の例では、最小2乗法などを使って 直接IIRフィルターのすべての係数を求めようとしても 上手くいかない。
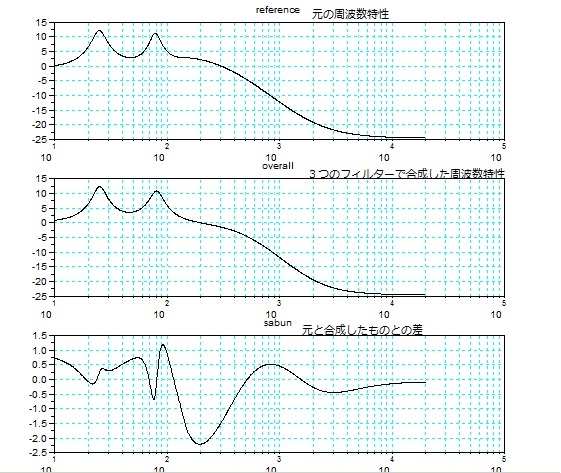
そこで、下図のように、山(ピーク)が2個あり、右下がりの特性を持つ元の周波数特性を、3個の固定フィルター(2個のピーキングフィルターと1個のシェルビングフィルター)を直列にして合成したもので 近似的に実現すること考えてみよう。
それぞれのフィルターの特性は Qとカットオフ周波数とゲインの3個のパラメーターで決定される。
ここでも、すべてのパラメーターをいっぺんに決めるのは難しい。そこで、適当な初期値からはじめて、個々のフィルターについて部分的にパラメーターを変化
させて、元の周波数特性と比較して差が小さくなるパラメーターの値を探す。これを個々のフィルターごとに何度か繰り返して、追い込んでいく。試行錯誤の計
算である。全体をいっぺんに変化させている訳ではないので、最適解にはならないが、不自然な値となって探索が失敗しないように、部分的に進める方法をとっ
ている。また、固定フィルターが存在する条件として、ゲインなどはある有限な値以上として(つまり、ゲインは零ではなく、6dB以上はあるとかなど)制約
を想定する。
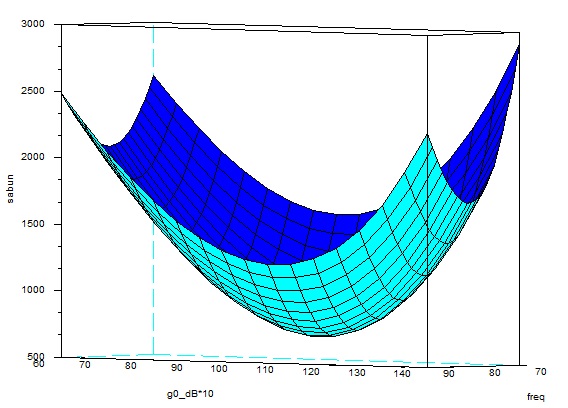
下図は、カットオフ周波数freqとゲインg0_dB(を10倍したスケール)について、解のありそうな変域で離散的に変化させたときの、
元の合成したフィルターの振幅(dB)の差の(対数スケールの周波数軸の)2乗和を縦軸に示したものである。
第1のフィルターのピーキングフィルターの特性と、Qとカットオフ周波数とゲインの値と、
Z変換の表現(SCILABではZのマイナス乗が不都合である。これに分子と分母にzの-2乗を掛けると 通常の表示になる。)
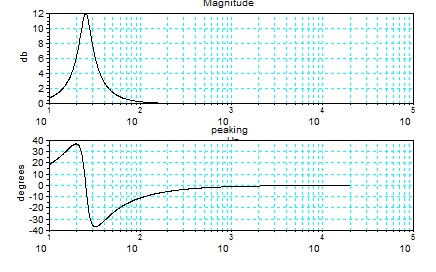
q01 =
4.
fc1 =
25.
g0_dB1 =
12.
xHd1 =
2
0.9977832 - 1.9990972z + 1.0013267z
-----------------------------------
2
0.9991099 - 1.9990972z + z
第2のフィルターのピーキングフィルターの特性と、Qとカットオフ周波数とゲインの値と、
Z変換の表現(SCILABではZのマイナス乗が不都合である。これに分子と分母にzの-2乗を掛けると 通常の表示になる。)
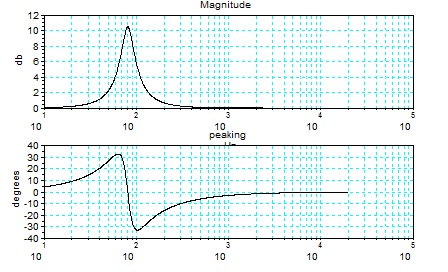
q02 =
3.76
fc2 =
80.365135
g0_dB2 =
10.5
xHd2 =
2
0.9933873 - 1.9968285z + 1.0035721z
-----------------------------------
2
0.9969594 - 1.9968285z + z
第3のフィルターの2次のシェルビングフィルターの特性と、Qとカットオフ周波数とゲインの値と、
Z変換の表現(SCILABではZのマイナス乗が不都合である。これに分子と分母にzの-2乗を掛けると 通常の表示になる。)
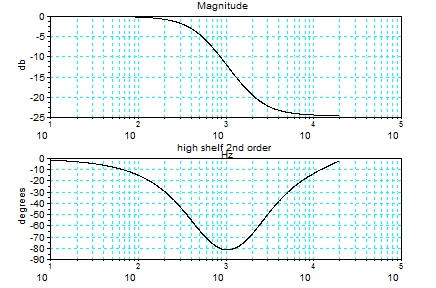
q03 =
0.561
fc3 =
2081.4805
g0_dB3 =
- 24.5
xHd3 =
2
0.0422908 - 0.1092754z + 0.0719342z
-----------------------------------
2
0.8785416 - 1.8735921z + z
3個のフィルターを合成した特性。
Z変換の表現(SCILABではZのマイナス乗が不都合である。これに分子と分母にzの-6乗を掛けると 通常の表示になる。)
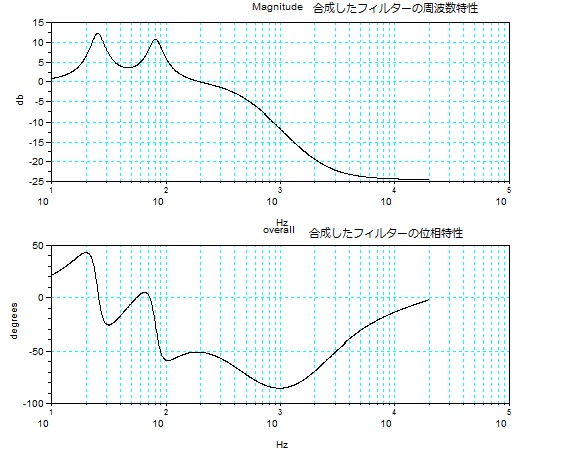
xHdall =
2
3
4
5
0.0419180 - 0.2765568z + 0.7592617z - 1.1099103z + 0.9109596z - 0.3979591z
6
+ 0.0722869z
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2
3
4
5
6
0.8750908 - 5.3699182z + 13.728729z - 18.717584z + 14.3532z - 5.8695179z + z
今回の3つのフィルターの合成の計算に使った数値演算ライブラリSCILAB用のサンプルプログラムを参考までに以下に紹介します。 このサンプルプログラムの動作保証はありませんのであしからず。
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// a study of high shelf and peaking filter by scilab-4.1.2
//
// ..............................................................................
// WARNING: This program may have some bugs and you may modify this program.
// Everything done by your own risk, if you use this program.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [wout]=souitizi_trans(fc0,fs)
wout = (fc0 / fs) * 2.0 * %pi;
wout = tan( wout /2.0);
wout = wout * 2.0 ;
endfunction
//--------------------------------------------------------
function [bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0,]=set_high_shelf_dig(fs,g0_dB,fc,q0)
// 2nd order filter
bunbo0=zeros(1,3);
bunsi0=zeros(1,3);
ibunbo0=zeros(1,3);
ibunsi0=zeros(1,3);
bx=zeros(1,3);
by=zeros(1,3);
g0= 10^(g0_dB/20.0);
if g0 > 0 then
if g0 < 1.0 then
g0=1.0/g0;
end
A=sqrt(g0);
else
disp('error: g0 is 0 or minus. set_high_shelf_dig');
A=1.0;
g0=1.0;
end
fc = fc / sqrt(sqrt(g0));
omega = souitizi_trans( fc, fs);
sn = sin(omega);
cs = cos(omega);
//alpha = sn / (2.0 * q0);
beta0 = sqrt(sqrt(g0)) / q0;
bx(1) = A * ((A + 1.0) + (A - 1.0) * cs + beta0 * sn);
bx(2) = - 2.0 * A * ((A - 1.0) + (A + 1.0) * cs);
bx(3) = A * ((A + 1.0) + (A - 1.0) * cs - beta0 * sn);
by(1) = (A + 1.0) - (A - 1.0) * cs + beta0 * sn;
by(2) = 2.0 * ((A - 1.0) - (A + 1.0) * cs);
by(3) = (A + 1.0) - (A - 1.0) * cs - beta0 * sn;
//
if g0_dB >= 0.0 then
bunbo0 = by ./ by(1);
bunsi0 = bx ./ by(1);
else
bunbo0 = bx ./ bx(1);
bunsi0 = by ./ bx(1);
end
for i=1:3
ibunbo0(3-i+1)=bunbo0(i);
ibunsi0(3-i+1)=bunsi0(i);
end
//
endfunction
//----------------------------------------------------------------
function [bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0,]=set_peaking1_dig(fs,g0_dB,fc,q0)
// 2nd order filter type1
bunbo0=zeros(1,3);
bunsi0=zeros(1,3);
ibunbo0=zeros(1,3);
ibunsi0=zeros(1,3);
bx=zeros(1,3);
by=zeros(1,3);
g0= 10^(g0_dB/20.0);
if g0 > 0 then
if g0 < 1.0 then
g0=1.0/g0;
end
A=sqrt(g0);
q0=q0 / A;
else
disp('error: g0 is 0 or minus. set_peaking1_dig');
A=1.0;
g0=1.0;
end
omega = souitizi_trans( fc, fs);
sn = sin(omega);
cs = cos(omega);
alpha = sn / (2.0 * q0);
//beta0 = sqrt(sqrt(g0)) / q0;
bx(1) = 1.0 + alpha * A;
bx(2) = - 2.0 * cs;
bx(3) = 1.0 - alpha * A;
by(1) = 1.0 + alpha / A;
by(2) = - 2.0 * cs;
by(3) = 1.0 - alpha / A;
//
if g0_dB >= 0.0 then
bunbo0 = by ./ by(1);
bunsi0 = bx ./ by(1);
else
bunbo0 = bx ./ bx(1);
bunsi0 = by ./ bx(1);
end
for i=1:3
ibunbo0(3-i+1)=bunbo0(i);
ibunsi0(3-i+1)=bunsi0(i);
end
//
endfunction
//----------------------------------------------------------------
function [bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0,]=set_peaking2_dig(fs,g0_dB,fc,q0)
// 2nd order filter type2
bunbo0=zeros(1,3);
bunsi0=zeros(1,3);
ibunbo0=zeros(1,3);
ibunsi0=zeros(1,3);
bx=zeros(1,3);
by=zeros(1,3);
g0= 10^(g0_dB/20.0);
if g0 > 0 then
if g0 < 1.0 then
g0=1.0/g0;
end
A=sqrt(g0);
else
disp('error: g0 is 0 or minus. set_peaking2_dig');
A=1.0;
g0=1.0;
end
g0 = souitizi_trans( fc, fs) / 2.0;
bx(1) = 1.0 + ( g0 / (A * q0)) + g0 * g0;
bx(2) = 2.0 * ( g0 * g0 - 1.0);
bx(3) = g0 * g0 - (g0 / (A * q0)) + 1.0;
by(1) = 1.0 + ( g0 * A / q0) + g0 * g0;
by(2) = 2.0 * ( g0 * g0 - 1.0);
by(3) = g0 * g0 - (g0 * A / q0) + 1.0;
//
if g0_dB < 0.0 then
bunbo0 = by ./ by(1);
bunsi0 = bx ./ by(1);
else
bunbo0 = bx ./ bx(1);
bunsi0 = by ./ bx(1);
end
for i=1:3
ibunbo0(3-i+1)=bunbo0(i);
ibunsi0(3-i+1)=bunsi0(i);
end
//
endfunction
//----------------------------------------------------------------
// MISC function for display
fs=44100;
start_freq0=10.0;
end_freq0=20000.0;
step_freq0=1000.0; // many is good
scale_mode0=1; // 0 linear, 1 log
function [freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs(start_freq,end_freq,step_freq,scale_mode)
//
mode0=scale_mode;
if end_freq > (1.1 * (fs/2.0)) then
end_freq= 0.9 * (fs/2.0);
end
if mode0==0 then // linear scale
step_freq=(end_freq-start_freq)/step_freq;
freqa=(start_freq:step_freq:end_freq);
freqd=((start_freq/fs):(step_freq/fs):(end_freq/fs));
end
if mode0==1 then // log scale
step0= (log(end_freq) - log(start_freq)) / step_freq;
bairitu0= exp( step0 );
freqa=zeros(1,2);
freqd=zeros(1,2);
freqa(1)=start_freq;
freqd(1)=freqa(1)/fs;
for v=1:int(step_freq)
freqa(v+1)=freqa(v) * bairitu0;
freqd(v+1)=freqa(v)/fs;
end
end
s0=size(freqa);
kosuu=s0(1,2);
endfunction
//--------------------------------------------------------
//========================================================
// read reference point data
disp('load data...');
exec("f_data1.sci"); // frequecny list, 1 means fs/2, half of sampling frequecny
exec("H_data1.sci"); // gain list
//
s0=size(f);
fscale0=0.5;
[freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs(start_freq0,end_freq0,step_freq0,scale_mode0);
c0=1;
dbr=zeros(1,kosuu);
phir=zeros(1,kosuu);
for k=1:kosuu
for v=c0:(s0(1)-1)
if (freqd(k) >= (f(v) * fscale0)) & (freqd(k) <= (f(v+1) * fscale0)) then
// liner interpolation of frequency response
dbr(k)=( (H(v+1) - H(v)) / (f(v+1) - f(v) )) * ( (freqd(k) / fscale0) - f(v) ) + H(v);
dbr(k)=20.0 * log10( dbr(k));
phir(k)=0;
c0=v;
break;
end
end
end // k
//========================================================
// 1st filter peaking
q01=4.0;
fc1=25.0;
g0_dB1=12;
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_peaking1_dig(fs,g0_dB1,fc1,q01);
bunbo1=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi1=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd1=syslin('d',bunsi1,bunbo1); // digital discrete time system
// 2nd filter peaking
q02=4.0;
fc2=87.0;
g0_dB2=9.0;
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_peaking1_dig(fs,g0_dB2,fc2,q02);
bunbo2=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi2=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd2=syslin('d',bunsi2,bunbo2); // digital discrete time system
// 3rd filter high shelf 2nd order
q03=0.6;
fc3=800.0;
g0_dB3=-25;
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_high_shelf_dig(fs,g0_dB3,fc3,q03);
bunbo3=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi3=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd3=syslin('d',bunsi3,bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
// over-all
xHdall= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2 * bunsi3, bunbo1 * bunbo2 * bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
//==========================================================================
wm0 = ones(kosuu,1); // measure weights (here all equal to 1...)
kousa = 0.5; // 目標とする許容誤差 dB この範囲の差e はゼロとして評価する
//..................................................................................
// y= yth3(freqd,x0);
function y = yth3(t, x)
fsv=fs;
g0_dBv=x(1);
fcv=x(2);
q0v=x(3);
freqdv=t;
[bunbo0v,bunsi0v,ibunbo0v,ibunsi0v]=set_high_shelf_dig(fsv,g0_dBv,fcv,q0v);
bunbo3v=poly(ibunbo0v,'z','coeff');
bunsi3v=poly(ibunsi0v,'z','coeff');
// over-all
xHdallv= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2 * bunsi3v, bunbo1 * bunbo2 * bunbo3v); // digital discrete time system
[frq0v, repf0v]=repfreq(xHdallv,freqdv);
[db0v,phi0v]=dbphi(repf0v);
y=db0v;
endfunction
// e= myfun3( x0, freqd,dbr, wm0);
function e = myfun3(x, tm, ym, wm)
e = wm.*( yth3(tm, x) - ym )';
for i=1:length(e)
if abs(e(i)) < kousa then
e(i)=0.0;
end
end
endfunction
//....................................................................................
// y= yth2(freqd,x0);
function y = yth2(t, x)
fsv=fs;
g0_dBv=x(1);
fcv=x(2);
q0v=x(3);
freqdv=t;
[bunbo0v,bunsi0v,ibunbo0v,ibunsi0v]=set_peaking1_dig(fsv,g0_dBv,fcv,q0v);
bunbo2v=poly(ibunbo0v,'z','coeff');
bunsi2v=poly(ibunsi0v,'z','coeff');
// over-all
xHdallv= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2v * bunsi3, bunbo1 * bunbo2v * bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
[frq0v, repf0v]=repfreq(xHdallv,freqdv);
[db0v,phi0v]=dbphi(repf0v);
y=db0v;
endfunction
//
function e = myfun2(x, tm, ym, wm)
e = wm.*( yth2(tm, x) - ym )';
for i=1:length(e)
if abs(e(i)) < kousa then
e(i)=0.0;
end
end
endfunction
//....................................................................................
//
function display0( winno)
xset('window',winno); // create new windows
clf();
subplot(311);
gainplot(freqa, dbr,phir);
xtitle('reference');
subplot(312);
[frq0, repf0]=repfreq(xHdall,freqd);
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(repf0);
gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
xtitle('overall');
subplot(313);
gainplot(freqa,db0 - dbr, phi0 - phir);
xtitle('sabun');
endfunction
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INIT_DISPLAY0=1;
if INIT_DISPLAY0 == 1 then
display0(10);
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 1st filterと2nd filterは とりあえず 初期値のままで
// 3rd filter high shelf 2nd orderのゲインは固定しておいて、 fcとqを可変して あう所さ探る
//
[freqa3, freqd3, kosuu3]=get_freqs(500,4000,40,1);
q03_range=0.1:0.05:1;
size_q03=length(q03_range);
matrix3=zeros(kosuu3,size_q03);
x0=zeros(1,3);
disp_stepx=10;
for loop1=1:kosuu3
if modulo(loop1,disp_stepx) == 1 then
disp( loop1 );
end
for loop2=1:size_q03
x0(1)=g0_dB3;
x0(2)=freqa3(loop1);
x0(3)=q03_range(loop2);
e= myfun3( x0, freqd,dbr, wm0);
matrix3(loop1,loop2)= e' * e;
end
end
[m0,n0]=min(matrix3);
m0
fc3=freqa3(n0(1))
q03=q03_range(n0(2))
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_high_shelf_dig(fs,g0_dB3,fc3,q03);
bunbo3=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi3=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd3=syslin('d',bunsi3,bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
// over-all
xHdall= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2 * bunsi3, bunbo1 * bunbo2 * bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
COUNT1_DISPLAY0=1
if COUNT1_DISPLAY0 == 1 then
xset('window',11); // create new windows
clf();
plot3d(freqa3,q03_range *1000,matrix3,leg="freq@q0*1000@sabun");
display0(12);
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 次に
// 2nd filter peakingのqは固定しておいて、 ゲインとfcを可変して あう所さ探る
//
[freqa2, freqd2, kosuu2]=get_freqs(70,90,20,1);
g0_dB2_range=6.0:0.5:14.0;
size_g0_dB2=length(g0_dB2_range);
matrix2=zeros(kosuu2,size_g0_dB2);
x0=zeros(1,3);
for loop1=1:kosuu2
if modulo(loop1,disp_stepx) == 1 then
disp( loop1 );
end
for loop2=1:size_g0_dB2
x0(1)=g0_dB2_range(loop2);
x0(2)=freqa2(loop1);
x0(3)=q02;
e= myfun2( x0, freqd,dbr, wm0);
matrix2(loop1,loop2)= e' * e;
end
end
[m0,n0]=min(matrix2);
m0
fc2=freqa2(n0(1))
g0_dB2=g0_dB2_range(n0(2))
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_peaking1_dig(fs,g0_dB2,fc2,q02);
bunbo2=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi2=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd2=syslin('d',bunsi2,bunbo2); // digital discrete time system
// over-all
xHdall= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2 * bunsi3, bunbo1 * bunbo2 * bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
COUNT2_DISPLAY0=1;
if COUNT2_DISPLAY0 == 1 then
xset('window',13); // create new windows
clf();
plot3d(freqa2,g0_dB2_range *10,matrix2,leg="freq@g0_dB*10@sabun");
display0(14);
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 再度、
// 3rd filter high shelf 2nd orderのゲインは固定しておいて、
// fcとqを可変して より細かく 探る。
ratio3=0.2; // 可変範囲
[freqa3, freqd3, kosuu3]=get_freqs((fc3 * (1.0 -ratio3)) , (fc3 * (1.0 + ratio3)), 40,1);
q03_range=(q03 * (1.0 - ratio3)):(q03 * 2.0 * ratio3 / 20):(q03 * (1.0 + ratio3));
size_q03=length(q03_range);
matrix3=zeros(kosuu3,size_q03);
x0=zeros(1,3);
for loop1=1:kosuu3
if modulo(loop1,disp_stepx) == 1 then
disp( loop1 );
end
for loop2=1:size_q03
x0(1)=g0_dB3;
x0(2)=freqa3(loop1);
x0(3)=q03_range(loop2);
e= myfun3( x0, freqd,dbr, wm0);
matrix3(loop1,loop2)= e' * e;
end
end
[m0,n0]=min(matrix3);
m0
fc3=freqa3(n0(1))
q03=q03_range(n0(2))
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_high_shelf_dig(fs,g0_dB3,fc3,q03);
bunbo3=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi3=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd3=syslin('d',bunsi3,bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
// over-all
xHdall= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2 * bunsi3, bunbo1 * bunbo2 * bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
COUNT3_DISPLAY0=1;
if COUNT3_DISPLAY0 == 1 then
xset('window',15); // create new windows
clf();
plot3d(freqa3,q03_range *1000,matrix3,leg="freq@q0*1000@sabun");
display0(16);
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 再々
// 3rd filter high shelf 2nd orderのq は固定しておいて、
// fc と ゲインを可変して 探る。
ratio3=0.2; // 可変範囲
[freqa3, freqd3, kosuu3]=get_freqs((fc3 * (1.0 -ratio3)) , (fc3 * (1.0 + ratio3)), 40,1);
//q03_range=(q03 * (1.0 - ratio3)):(q03 * 2.0 * ratio3 / 20):(q03 * (1.0 + ratio3));
//size_q03=length(q03_range);
g0_dB3_range=-27:0.5:-23;
size_g0_dB3=length(g0_dB3_range);
matrix3=zeros(kosuu3,size_g0_dB3);
x0=zeros(1,3);
for loop1=1:kosuu3
if modulo(loop1,disp_stepx) == 1 then
disp( loop1 );
end
for loop2=1:size_g0_dB3
x0(1)=g0_dB3_range(loop2);
x0(2)=freqa3(loop1);
x0(3)=q03;
e= myfun3( x0, freqd,dbr, wm0);
matrix3(loop1,loop2)= e' * e;
end
end
[m0,n0]=min(matrix3);
m0
fc3=freqa3(n0(1))
g0_dB3=g0_dB3_range(n0(2))
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_high_shelf_dig(fs,g0_dB3,fc3,q03);
bunbo3=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi3=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd3=syslin('d',bunsi3,bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
// over-all
xHdall= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2 * bunsi3, bunbo1 * bunbo2 * bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
COUNT4_DISPLAY0=1;
if COUNT4_DISPLAY0 == 1 then
xset('window',17); // create new windows
clf();
plot3d(freqa3,g0_dB3_range *100,matrix3,leg="freq@g0_dB*100@sabun");
display0(18);
end
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 再度
// 2nd filter peakingのゲインは固定しておいて、
// fcとqを可変して より細かく 探る。
ratio2=0.2; // 可変範囲
[freqa2, freqd2, kosuu2]=get_freqs((fc2 * (1.0 -ratio2)) , (fc2 * (1.0 + ratio2)), 40,1);
q02_range=(q02 * (1.0 - ratio2)):(q02 * 2.0 * ratio2 / 20):(q02 * (1.0 + ratio2));
size_q02=length(q02_range);
matrix2=zeros(kosuu2,size_q02);
x0=zeros(1,3);
for loop1=1:kosuu2
if modulo(loop1,disp_stepx) == 1 then
disp( loop1 );
end
for loop2=1:size_q02
x0(1)=g0_dB2;
x0(2)=freqa2(loop1);
x0(3)=q02_range(loop2);
e= myfun2( x0, freqd,dbr, wm0);
matrix2(loop1,loop2)= e' * e;
end
end
[m0,n0]=min(matrix2);
m0
fc2=freqa2(n0(1))
q02=q02_range(n0(2))
[bunbo0,bunsi0,ibunbo0,ibunsi0]=set_peaking1_dig(fs,g0_dB2,fc2,q02);
bunbo2=poly(ibunbo0,'z','coeff');
bunsi2=poly(ibunsi0,'z','coeff');
xHd2=syslin('d',bunsi2,bunbo2); // digital discrete time system
// over-all
xHdall= syslin('d',bunsi1 * bunsi2 * bunsi3, bunbo1 * bunbo2 * bunbo3); // digital discrete time system
COUNT5_DISPLAY0=1;
if COUNT5_DISPLAY0 == 1 then
xset('window',19); // create new windows
clf();
plot3d(freqa2,q02_range *10,matrix2,leg="freq@q0*10@sabun");
display0(20);
end
//====================================================================================
DISP_EACH_FILTERS=1;
if DISP_EACH_FILTERS == 1 then
//***
//wb0=xget('window'); // stack old window
//***
w0=0;
xset('window',w0); // create new windows
clf();
//[freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs();
//[frq0, repf0]=repfreq(xHd1,freqd);
//[db0,phi0]=dbphi(repf0);
//gainplot(freqa,dbr,phir);
bode(freqa, dbr,phir);
xtitle('reference');
w0=w0+1;
xset('window',w0); // create new windows
clf();
//[freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs();
[frq0, repf0]=repfreq(xHd1,freqd);
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(repf0);
//gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
bode(freqa, db0,phi0);
xtitle('peaking');
q01
fc1
g0_dB1
xHd1
w0=w0+1;
xset('window',w0); // create new windows
clf();
[frq0, repf0]=repfreq(xHd2,freqd);
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(repf0);
//gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
bode(freqa, db0,phi0);
xtitle('peaking');
q02
fc2
g0_dB2
xHd2
w0=w0+1;
xset('window',w0); // create new windows
clf();
[frq0, repf0]=repfreq(xHd3,freqd);
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(repf0);
//gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
bode(freqa, db0,phi0);
xtitle('high shelf 2nd order');
q03
fc3
g0_dB3
xHd3
w0=w0+1;
xset('window',w0); // create new windows
clf();
[frq0, repf0]=repfreq(xHdall,freqd);
[db0,phi0]=dbphi(repf0);
//gainplot(freqa,db0,phi0);
bode(freqa, db0,phi0);
xtitle('overall');
xHdall
//***
//xset('window',wb0);
//***
end //if DISP_EACH0 == 1 then
No.3 2020年5月10日









