Estimation of vocal tract as two tubes model or three tubes model
This is a trial estimation of vocal tract as simple tube model, two tubes model or three tubes model,
using several peak and drop-peak frequencies of vowel voice,
by precomputed grid search and downhill simplex method.
Two tubes model
Two tubes model is a very simplified model of vocal tract.
As following figure, two tubes model is consisted of two tubes: one is length L1 cross-section area A1 and another is length L2 cross-section area A2.
This simplified model can't reproduce human voice completely, however, it's useful to understand the feature roughly.
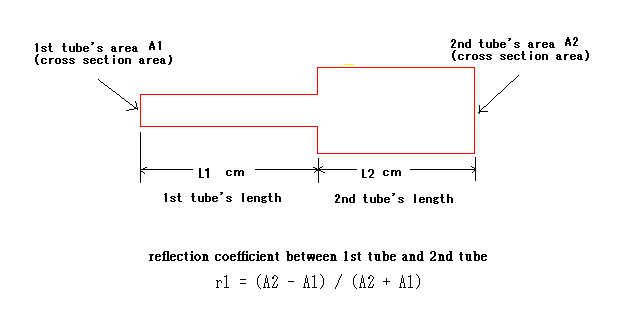
Reflection coefficient is defined by two cross-section area A1 and A2.
Estimation of two tubes model is identified by 3 parameters, L1, L2, and r1, matching with the observed signal.
Three tubes model is a model in which one tube is added to two tubes model. Three tubes model is identified by 5 parameters, L1, L2, L3, r1, and r2.
Estimation method
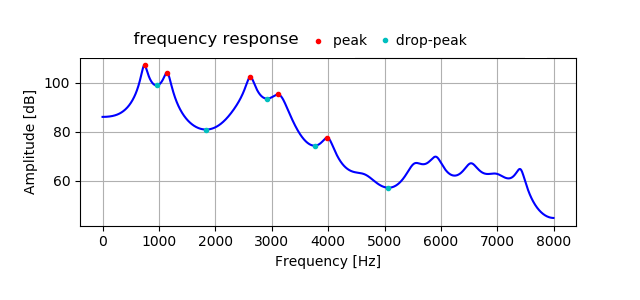
Following figure is an example of frequency response of vowel voice based on LPC analysis.
Red dot is peak (this is sometime called formant frequency) and blue dot is local bottom (here, it's called as drop-peak).
Estimation is to find suitable parameters whose peak and drop-peak frequencies value are as close as possible,
comparing frequency response of real voice and two tubes model or three tubes model.
In general, it's difficult to uniquely determine the shape of vocal tract from voice.
So, here, following constraint conditions are placed on.
- As evaluation values, 2 peak frequencies and 2 drop-peak frequencies in ascending order are used. (for three tubes model, 3 peak and drop-peak are used.)
- As consideration of mouth cavity opening shape availability, reflection coefficient is limited between -0.9 and 0.9.
- For two tubes model, length L1 should be equal to or larger than L2. This reason is that
in many cases, peak and drop-peak frequency becomes close between replacement of L1 and L2.
(There are also exceptions.) It's a choice one of similar.
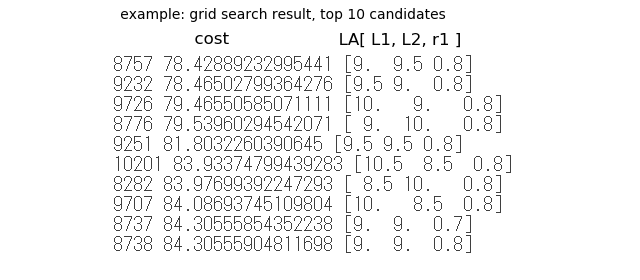
Following is an example of grid search result of cost (frequencies difference) minimum top 10.
The candidate which replaced L1 and L2 is arranged in order.
- For vowel voice /o/ case, three tubes model is applied and r1 should be 0 or more (A2 is bigger than A1).
Estimation is performed in two steps: a grid search that computes representative grid points using precomputed data in advance, and then detailed search that uses the candidate of grid search as an initial value.
Estimation result
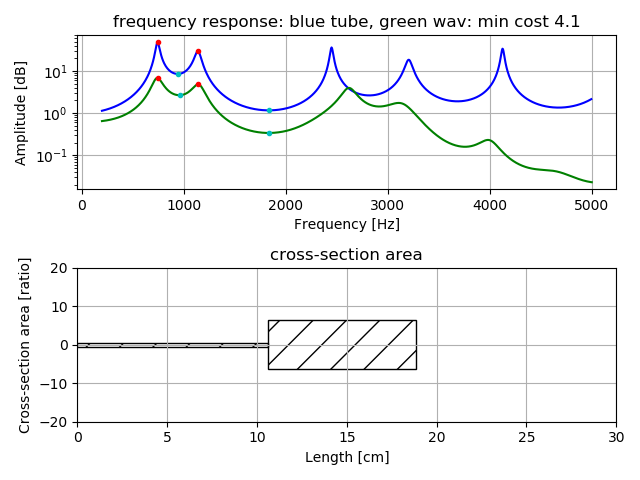
Following figures are estimation result for vowel voice when uttered alone.
Upper is comparison of frequency response by tubes model (blue color) with
frequency response by real voice (green color). Lower shows length and cross-section area of the tube model.
Example of estimation two tubes model for vowel voice /a/
Example of estimation two tubes model for vowel voice /i/
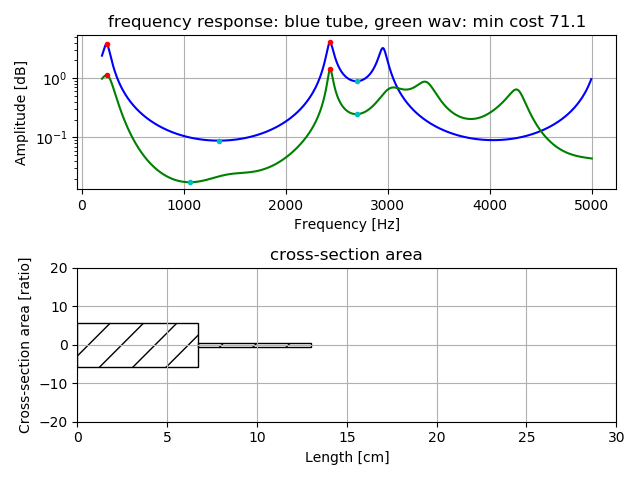
Example of estimation two tubes model for vowel voice /u/
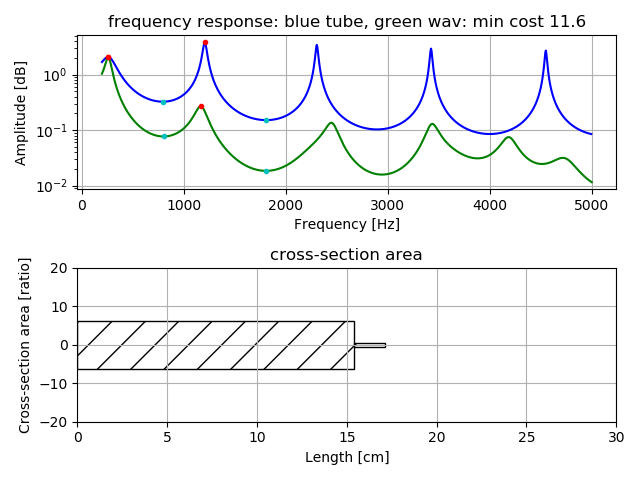
Example of estimation two tubes model for vowel voice /e/
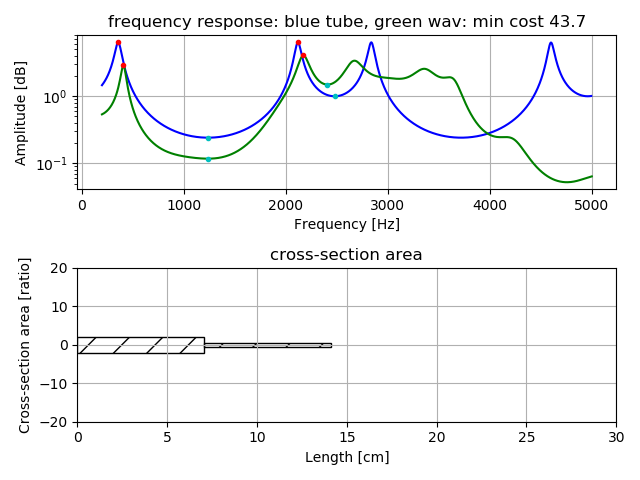
Example of estimation three tubes model for vowel voice /o/
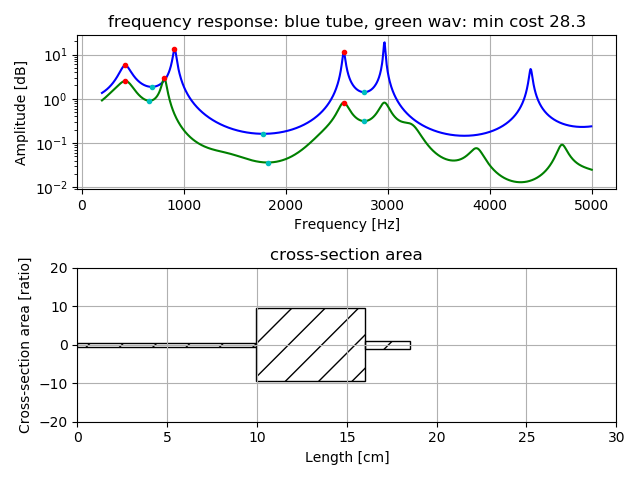
For reference, there is Python program to compute above by Python. Please see README.txt in the zip file about usage.
No.1b, 26 March 2019
Home page







