ディエンファ
シス(de-emphasis)IIR フィルタ ─数値計算ソフトのSCILABを使って係数の計算─
むかし、アナログ機器の時代、録音機の特性がまだよくなかったころ、試聴時のノイズ感を少なくするため、わざと音の高い高域の成分を大きく録音しておい
て、再生するときには逆に高域の成分を小さく再生すること(ディエンファシス、強調の逆と言う意味)で、ノイズ感を改善することがおこなわれていた。デジ
タル機器に進化した現在でも、CDやMP3ファイルの中には、実際には
あまり使われていないかもしれないが、ディエンファシスをOFF/ONするための設定が
残されている。(MP3でエンファシスを設定
したサンプルデータ)
もともと、ディエンファシスはアナログフィルター回路の時定数で定義されていた。例えば、CDのディエンファシス フィルターの時定数は、
50/15uSである。このアナログの時定数50/15uSに相当する、IIRデジタルフィルタの係数を計算してみた。サンプリング周波数がCDと同じ
44.1KHzのときの、1次のIIRフィルターの係数である。IIRのフィルターの計算をC言語風に書いてみた。 デジタルフィルターでは、サンプリン
グ周波数が違うとフィルターの係数の値も違うので注意してほしい。
int i;
double a[2],b[2],w[2];
#define NUMBER xxxx <=データの個数を設定する。
double in0[NUMBER],out0[NUMBER];
/* 1次 IIR ディエンファシス フィルター
*/
/* アナログの時定数1 = 50uS
*/
/* アナログの時定数2 = 15uS
*/
/* サンプリング周波数 44.100KHz
*/
/* フィルターの係数 a[], b[]
*/
a[1]=0.6303142;
b[0]=0.4599584;
b[1]=-0.0902726;
/* 直接形2
*/
/* in[i] 入力 out[i] 出力
*/
/* w[] は前の計算データを保持しておくための記憶域 。他の用途に使わないこと。 */
/* w[1]=0.0 は ゼロに初期化してから使うこと。
*/
w[1] = 0.0;
for (i=0; i< NUMBER ; ++i)
{
w[0] = in0[i] + a[1] * w[1];
out0[i] = b[0] * w[0] + b[1] * w[1];
w[1] = w[0];
}
もうひとつの例として
int i;
double a[2],b[2],wi[2],wo[2];
#define NUMBER xxxx <=データの個数を設定する。
double in0[NUMBER],out0[NUMBER];
/* 1次 IIR ディエンファシス フィルター
*/
/* アナログの時定数1 = 50uS
*/
/* アナログの時定数2 = 15uS
*/
/* サンプリング周波数 44.100KHz
*/
/* フィルターの係数 a[], b[]
*/
a[1]=0.6303142;
b[0]=0.4599584;
b[1]=-0.0902726;
/* 直接形 1
*/
/* in[i] 入力 out[i] 出力
*/
/* wi[],wo[] は前の計算データを保持しておくための記憶域 。他の用途に使わないこと。 */
/* wi[1]=0.0 wo[1]=0.0は ゼロに初期化してから使うこと。
*/
wi[1] = 0.0;
wo[1] = 0.0;
for (i=0; i< NUMBER ; ++i)
{
out0[i] = b[0] * in0[i] + b[1] * wi[1] + a[1]
*
wo[1];
wi[1] = in0[i];
wo[1] = out0[i];
}
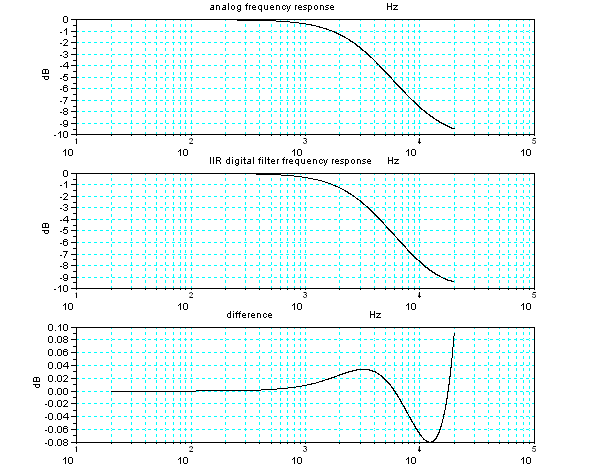
もともと、アナログフィルターとデジタルフィルターはまったく同じではないので、下図の様に周波数特性に違いが出てしまう。一番上がアナログフィルターの
周波数特性で、2番目がこんかいのデジタルフィルターで、一番下がアナログとデジタルの差である。1dBぐらいの差であると音の
レベルの違いは判ってしまうが、こんかいは差は小さいので実用的には問題ないレベルではないかと思う。
一般的に、係数を有限なBIT数に変換したり、有限なBIT数での乗算と加算を計算するときに演算誤差が発生する。(参考)
さて、フランス発の数値演算ライブラリ SCILAB を使ってディエン
ファシス(de-emphasis)IIR
フィルタの係数を計算するサンプルプログラム(de-emphasis.sci)を作ってみたので紹介しよう。
1次のフィルターは双線形変換で求めたが、アナログの時定数2のほうを手動で補正してアナログとの差が小さくなるように合わせこんでいる(15uの方を
12.5%増しで計
算している)ので、50/15uをそのまま双線形変
換した値とは異なっている。双線形変換の場合、アナログとデジタルの間で、周波数がリニアに変換されず、たかめの周波数ではアナログとデジタルの周波数の
違いが大きくなる。そこで、今回は、高い周波数の方の15uの値を手動で特性の差が小さくなるように調整した。
また、2次以上のフィルターの計算では、scilabのleast-squareの関数(たぶん、アナログとデジタルの振幅特性の2乗差が小さくなるよう
に、係数を探索するアルゴリズム)を使用している。
はじめに 変換の方法をひとつ選ぶ。
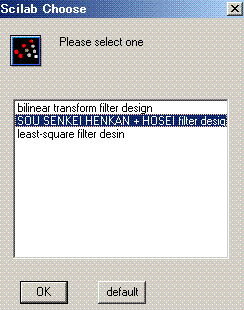
上右側にあるstep1 の(1)で値の設定、
step1 の(2)でIIRの係数を求めて周波数特性を描く。
step2の
(1)でフィルターの安定性の確認を行う。
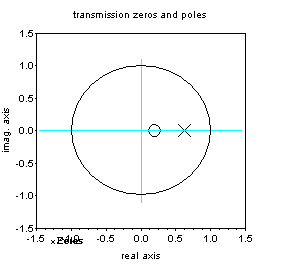
極 ポール pole Xと、零点 zero ○を 求めて、極 pole Xがおおきさ1の単位円の内側に入っていることを確認する。
step2の
(2)では、実際にSCILABを使って、振幅が1のSIN波をつくり それを入力としてIIRフィルタに入れたときの出力を計算して、理論値と計算値に
違いがないかを確認できる。
たかめの周波数の信号になると、信号に対してサンプリングの間隔が荒くなってしまうため、SIN波をサンプリングするとSIN波の形とはだいぶ違ったもの
になる。下図のXマークがついたところが、16KHzのSIN波をサンプリングした例である(サンプリング周波数は44.1KHz)。
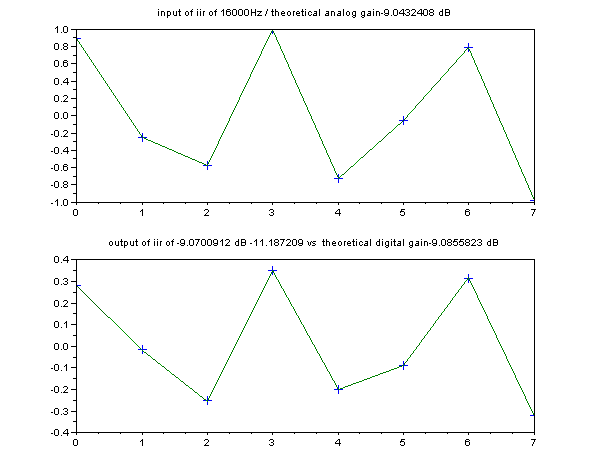
サンプリングされたデジタル信号からの振幅の推定は、
サンプリングされたものから最小2乗法を使って ちょうどピッタリ合う連続的なSIN波を求めることで、IIRフィルターの出力の振幅を推定している。上
図は、16000Hzの、デジタルフィルターの利得の理論値が-9.0855823dBに対して、IIRの出力は-9.0700912dBとなっている一
例である。
但し、過渡的な部分等で、見かけ上 DC成分が存在しているように見える場合もあるが、ここではDC成分の補正はしていない。
step3では、ここで求めたIIRのフィルターの係数をテキストファイルに書き出すものである。
実用的には、多段のフィルターは2次のIIRフィルターの組み合わせで合成されることがあるが、ここでは、2次フィルターで分割した形式のものにはなって
いない。(バンドパスフィルターを4つの2次フィルターで構成したときの例。 ずらしたピークを組み合わ
せることで全体の特性を出している。)
step4では、一番はじめだけ1でそれ以降はすべて零の値(インパルス)を入力したときの出力の波形を見ることができる。入出力の動作チェックにも使え
るかもしれない。 (インパルスの波形の一例)
step5では、実際にIIRフィルターの音を聞いてみようと言うもので、.wavファイルの頭の30秒だけ読み込んで(maxdurationで長さを
設定する)、フィルターを計算して、また、.
wavファイルに書き出すものである。step5は、scilabのバージョン、OSの種類、サウンド・デバイス、PCのメモリー容量などに依存している
ので、も
しかしたら動かないかもしれない。また、計算に少々時間がかかる。
このサンプルを実際に動作させるためには、
ご使用されるプログラミング環境に合わせて修正・変更・追加などが必要かもしれません。
また、バグが含まれている可能性があります。
万一、このサンプルを動作させる場合は、あなたの責任でおこなってくださいね。
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// IIR digital de-emphasis filter design
// as almost same as analog de-emphasis filter 50/15uS
//
// for window scilab-4.1.2
//
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PLEASE PAY ATTENTION that this program may have some bugs and also
you may modify program
// to fit your circumstances.
// If you use this program, everything should be done by your own risk.
// Thanks.
//===========================================================================================
// global variables No. 1
c50=50.0; // constant 1
c15=15.0; // constant 2
fs=44100.0; // sampling frequency
iiro=4; // oder of iir filter
start_freq=20.0;
end_freq=20000.0;
step_freq=1000.0; // many is good
scale_mode=0; // 0 linear, 1 log
trans_mode=1; // 0 least-square filter design, 1 bilinear
transform (= SOU SENKEI HENKAN in jappanese ) filter design
c15_change=0.0; // c15 = c15 * (1.0 + c15_change/100) This is available
only when trans_mode=1
//
z=poly(0,'z');
H1=z/(z-.5);
H0=syslin('d',H1); // dummy set, digital discrete time system
s=poly(0,'s');
S1=(1+2*s)/s^2;
S1A=syslin('c',S1); // dummy set, analog continuous time
system
//
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// choose trans_mode
SEL_CODE=x_choose(['bilinear transform filter design'; 'SOU SENKEI
HENKAN + HOSEI filter design'; 'least-square filter desin'],['Please
select one'],'default');
if SEL_CODE == 1 then
trans_mode=1;
elseif SEL_CODE == 2 then
trans_mode=1;
c15_change=12.5;
disp('message: constant 2 correction factor is set 12.5');
elseif SEL_CODE == 3 then
trans_mode=0;
else
trans_mode=1;
end
if trans_mode == 0 then
disp('least-square filter design');
elseif trans_mode == 1 then
disp('bilinear transform (= SOU SENKEI HENKAN in jappanese )
filter design');
end
//
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [wc50, wc15, wfs, wiiro, wc15_change]= set_constant()
if trans_mode==0 then
// 0 least-square filter design,
txt1=['constant 1 (default 50us)';'constant 2 (default 15us)';
'sampling frequency (default 44.1KHz)'; 'order of IIR filter'];
wstr1=sprintf('%f',c50);
wstr2=sprintf('%f',c15);
wstr3=sprintf('%f',fs);
wstr4=sprintf('%d',iiro);
sig1=x_mdialog('Input constant of analog de-emphasis filter,
sampling frequency and IIR order',txt1, [wstr1 ; wstr2 ; wstr3 ; wstr4
]);
if sig1==[] then
arg1=evstr(wstr1);
arg2=evstr(wstr2);
arg3=evstr(wstr3);
arg4=evstr(wstr4);
else
arg1=evstr(sig1(1));
arg2=evstr(sig1(2));
arg3=evstr(sig1(3));
arg4=evstr(sig1(4));
end
wc50=arg1;
wc15=arg2;
wfs=arg3;
wiiro=arg4;
wc15_change=0.0;
end //if trans_mode==0 then
//
//
//
if trans_mode==1 then
// 1 bilinear transform filter design
txt1=['constant 1 (default 50us)';'constant 2 (default 15us)';
'sampling frequency (default 44.1KHz)'; 'constant 2 correction factor
[%] (ex: 12.5)'];
wstr1=sprintf('%f',c50);
wstr2=sprintf('%f',c15);
wstr3=sprintf('%f',fs);
wstr4=sprintf('%f',c15_change);
sig1=x_mdialog('Input constant of analog de-emphasis filter,
sampling frequency and constant 2 correction factor ',txt1, [wstr1 ;
wstr2 ; wstr3; wstr4 ]);
if sig1==[] then
arg1=evstr(wstr1);
arg2=evstr(wstr2);
arg3=evstr(wstr3);
arg4=evstr(wstr4);
else
arg1=evstr(sig1(1));
arg2=evstr(sig1(2));
arg3=evstr(sig1(3));
arg4=evstr(sig1(4));
end
wc50=arg1;
wc15=arg2;
wfs=arg3;
wiiro=0;
wc15_change=arg4;
end //if trans_mode==1 then
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function factor0=correct_factor( wc15)
//
fc=1.0 / ( (wc15 * 0.000001) * 2.0 * %pi );
wd= (fc / (fs /2.0)) * %pi;
fcc=tan( wd / 2.0) * 2.0 / ( 1. / fs) / ( 2.0 * %pi);
factor0= (fc /fcc - 1.0 ) * 100.0; // beacause unit is [%]
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs()
//
mode0=scale_mode;
if end_freq > (1.1 * (fs/2.0)) then
end_freq= 0.9 * (fs/2.0);
end
if mode0==0 then // linear scale
step_freq=(end_freq-start_freq)/step_freq;
freqa=(start_freq:step_freq:end_freq);
freqd=((start_freq/fs):(step_freq/fs):(end_freq/fs));
end
if mode0==1 then // log scale
step0= (log(end_freq) - log(start_freq)) / step_freq;
bairitu0= exp( step0 );
freqa=zeros(1,2);
freqd=zeros(1,2);
freqa(1)=start_freq;
freqd(1)=freqa(1)/fs;
for v=1:int(step_freq)
freqa(v+1)=freqa(v) * bairitu0;
freqd(v+1)=freqa(v)/fs;
end
end
s0=size(freqa);
kosuu=s0(1,2);
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [wH0, wS1A , wiiro2]=filterdesign()
// analog_response
//
// dom='c' for a continuous time system,
// dom='d' for a discrete time system,
// n for a sampled system with sampling
period n (in seconds).
//
n-1
n-2
// B(z)
b(1)z + b(2)z + .... + b(n)
// H(z)= ---- = ---------------------------------
//
n-1 n-2
// A(z) z +
a(2)z + .... + a(n)
if trans_mode==0 then
// least-square filter design
//
s=poly(0,'s');
H1=(1+(c15 * 0.000001)*s)/(1+(c50 * 0.000001)*s),
wS1A=syslin('c',H1);
disp( wS1A );
//
[freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs();
[freqs, respa]=repfreq(wS1A, freqa);
freqz=zeros(1,2);
freqz(1)=0;
freqz(2)= fs /2.0;
[freqs, respz]=repfreq(wS1A, freqz);
wrespd=zeros(1,kosuu+2);
wfreqd=zeros(1,kosuu+2);
//
for v=1:kosuu
wrespd(v+1)= abs(respa(v));
wfreqd(v+1)= freqa(v) / (fs / 2.);
end
//
wrespd(1)=abs(respz(1));
wfreqd(1)=0.0;
wrespd(kosuu+2)=abs(respz(2));
wfreqd(kosuu+2)=1.0;
//
wH0=yulewalk(iiro,wfreqd,wrespd);
//
disp( wH0 );
end // if trans_mode==0 then
if trans_mode==1 then
// bilinear transform design
//
s=poly(0,'s');
H1=(1+(c15 * 0.000001)*s)/(1+(c50 * 0.000001)*s),
wS1A=syslin('c',H1);
disp( wS1A );
// bilinear transform from including correction factor
c15=c15 * ( 1.0 + c15_change/100.0);
H1=(1+(c15 * 0.000001)*s)/(1+(c50 * 0.000001)*s),
wS1A2=syslin('c',H1);
wS1Ass=tf2ss(wS1A2); //Now in state-space form
sl1=cls2dls(wS1Ass,1/fs); //sl1= output of cls2dls
wH0=ss2tf(sl1); // Converts in transfer form
disp( wH0 );
end // if trans_mode==1 then
[H0r,H0nx]=syssize( wH0 ); // get size
wiiro2=H0nx;
H0bunbo=denom( wH0 ); // get BUNBO
H0bunsi=numer( wH0 ); // get BUNSHI
//H0poles=roots( H0bunbo ); // get poles
//H0zeros=roots( H0bunsi ); // get zeros
[wcoeff_bunbo]=get_coeff( H0bunbo, wiiro2 );
[wcoeff_bunsi]=get_coeff( H0bunsi, wiiro2 );
//plzr( wH0 ); // plot zeros and poles
//
global ac0
global bcb0
global bc0
//
//disp('digital discrete time system');
//disp( H0nx );
//disp( '*bunbo/poles/x*');
//disp( H0bunbo);
//disp( wcoeff_bunbo(1), 'a[0] is always 1' );
for v=1:wiiro2
ac0(v)= - wcoeff_bunbo(v+1);
wstr1= 'a[' + string(v) + ']';
//disp( ac0(v), wstr1 );
end
//disp('poles are');
//disp( H0poles);
//disp( '*bunsi/zeros/o*')
//disp( H0bunsi);
bcb0=wcoeff_bunsi(1);
//disp( wcoeff_bunsi(1), 'b[0]' );
for v=1:wiiro2
bc0(v)= wcoeff_bunsi(v+1);
wstr1= 'b[' + string(v) + ']';
//disp( bc0(v), wstr1 );
end
//disp('zeros are');
//disp( H0zeros);
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function freq_response(disp0, sub0, H0, S1A)
//
wb0=xget('window'); // stack old window
xset('window',disp0); // create new windows
clf();
//
subplot(311);
[freqa, freqd, kosuu]=get_freqs();
[freqs,respa]=repfreq(S1A, freqa);
[db_fft1,phi_fft1] =dbphi(respa);
gainplot(freqa,db_fft1,phi_fft1);
wstr1 = 'analog frequency
response
Hz'
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','dB');
subplot(312);
[frq,respf]=repfreq(H0, freqd );
[db_fft2,phi_fft2] =dbphi(respf);
gainplot(freqa,db_fft2,phi_fft2);
wstr1 = 'IIR digital filter frequency
response Hz'
xtitle( wstr1,'','dB' );
subplot(313);
gainplot(freqa,(db_fft2-db_fft1),(phi_fft2-phi_fft1));
wstr1 =
'difference
Hz'
xtitle( wstr1,'','dB' );
//
xset('window',wb0); // push old windows
endfunction
//===============================================================================================================
// check routine
//
//
iiro2=0; // order of the IIR filter
mc0=10; // maximum order IIR filter quantity
global ac0
global bcb0
global bc0
global wk0
ac0=zeros(1,mc0); // coefficient matrix of a[1,..,mc0]
bcb0=zeros(1,1); // coefficient matrix of b[0]
bc0=zeros(1,mc0); // coefficient matrix of b[1,..,mc0]
wk0=zeros(1,mc0*2); // data stack memory
mc1=1; // maximum 1st order IIR filter quantity
global ac1
global bcb1
global bc1
global wk1
ac1=zeros(mc1,1); // coefficient matrix a[*][1]
bcb1=zeros(mc1,1); // coefficient matrix of b[*][0]
bc1=zeros(mc1,1); // coefficient matrix of b[*][1]
wk1=zeros(mc1,2); // data stack memory
mc2=5; // maximum 2nd order IIR filter cascade quantity
global ac2
global bcb2
global bc2
global wk2
ac2=zeros(mc2,2); // coefficient matrix of b[*][1,2]
bcb2=zeros(mc2,1); // coefficient matrix of b[*][0]
bc2=zeros(mc2,2); // coefficient matrix of b[*][1,2]
wk2=zeros(mc2,4); // data stack memory
//
freqx=5000.0; // Hz
cyclex=5;
skip_cyclex=2;
//
sin_delta=0.1; // dummy set
sin_level=1.0; // sin's level when actual IIR calculation
//
in0=zeros(1,1); // dummy set
out0=zeros(1,1); // dummy set
m=0; // dummy set // size of input
xopt0=zeros(1,2); // dummy set
xopt1=zeros(1,2); // dummy set
//
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [wcoeff]=get_coeff( wH0bunsi, wiiro2 )
//
z=poly(0,'z');
//
H0nx=wiiro2;
wcoeff=zeros(1,H0nx+1);
wcoeff(H0nx+1)= horner( wH0bunsi, 0.);
for v=1: H0nx
wH0bunsi=(wH0bunsi-wcoeff(H0nx+1-(v-1))) / z;
wcoeff(H0nx+1-v)= horner( wH0bunsi, 0.);
end
//
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [wiiro2]=system_stable_check( disp0, wH0, wS1A)
//
wb0=xget('window'); // stack old window
xset('window',disp0); // create new windows
clf();
[H0r,H0nx]=syssize( wH0 ); // get size
wiiro2=H0nx;
H0bunbo=denom( wH0 ); // get BUNBO
H0bunsi=numer( wH0 ); // get BUNSHI
H0poles=roots( H0bunbo ); // get poles
H0zeros=roots( H0bunsi ); // get zeros
[wcoeff_bunbo]=get_coeff( H0bunbo, wiiro2 );
[wcoeff_bunsi]=get_coeff( H0bunsi, wiiro2 );
plzr( wH0 ); // plot zeros and poles
//
global ac0
global bcb0
global bc0
//
disp('digital discrete time system');
disp( H0nx );
disp( '*bunbo/poles/x*');
disp( H0bunbo);
disp( wcoeff_bunbo(1), 'a[0] is always 1' );
for v=1:wiiro2
ac0(v)= - wcoeff_bunbo(v+1);
wstr1= 'a[' + string(v) + ']';
disp( ac0(v), wstr1 );
end
disp('poles are');
disp( H0poles);
disp( '*bunsi/zeros/o*')
disp( H0bunsi);
bcb0=wcoeff_bunsi(1);
disp( wcoeff_bunsi(1), 'b[0]' );
for v=1:wiiro2
bc0(v)= wcoeff_bunsi(v+1);
wstr1= 'b[' + string(v) + ']';
disp( bc0(v), wstr1 );
end
disp('zeros are');
disp( H0zeros);
//
//
xset('window',wb0); // push old windows
endfunction
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [wfreqx, wcycle, wskip_cycle]= set_synth()
//
txt1=['frequency [Hz]'; 'cycle (integral number)'; 'start
skip cycle (integral number)'];
wstr1=sprintf('%f',freqx);
wstr2=sprintf('%d',cyclex);
wstr3=sprintf('%d',skip_cyclex);
sig1=x_mdialog('do actual IIR filter calculation',txt1,
[wstr1 ; wstr2 ; wstr3 ]);
if sig1==[] then
arg1=evstr(wstr1);
arg2=evstr(wstr2);
arg3=evstr(wstr3);
else
arg1=evstr(sig1(1));
arg2=evstr(sig1(2));
arg3=evstr(sig1(3));
end
wfreqx=arg1;
wcycle=arg2;
wskip_cycle=arg3;
//
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [win0,wsin_delta,xm,xsm]= make_sin()
//
wsin_delta = freqx / fs * 2. * %pi;
xm= int( ((1.0/ freqx) / (1.0 /fs ) * cyclex) + 1.0);
xsm= int( ((1.0/ freqx) / (1.0 /fs ) * skip_cyclex) + 1.0);
win0=zeros(1,xm);
for v=1:xm
win0(v)= sin_level * sin( wsin_delta * (v-1));
end
//
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [win0,wout0,xm]=start_skip()
xm=m-sm;
win0=zeros(1,xm);
wout0=zeros(1,xm);
for v=(sm+1):m
win0( v - sm) = in0(v);
wout0( v - sm) = out0(v);
end
//
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [wout0]= cal_iir2(init_flag)
//
global wk0
if init_flag == 1 then
for v=1:(mc0*2)
wk0(v)=0.0;
end
end
//
//
wout0=zeros(1, m);
//
for i=1:m
w = in0(i);
for v=1:iiro2
w= w + ac0(v) * wk0(v);
wout0(i)= wout0(i) + bc0(v) * wk0(v);
end
wout0(i) = wout0(i) + bcb0 * w;
for v=1:(iiro2-1)
wk0( iiro2 - v + 1) = wk0( iiro2 - v);
end
wk0(1)=w;
end
//
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function plotfit(disp0)
wb0=xget('window'); // stack old window
xset('window',disp0); // create new windows
clf();
//
g0= 20.0 * log10( xopt1(1) / xopt0(1));
ph0= 360 * (xopt1(2)-xopt0(2))/2./%pi
//
freqa=[freqx,freqx];
freqd=[(freqx/fs),(freqx/fs)];
[freqs,respa]=repfreq(S1A, freqa);
[db_fft1,phi_fft1] =dbphi(respa);
[frq,respf]=repfreq(H0, freqd );
[db_fft2,phi_fft2] =dbphi(respf);
//
subplot(211);
tm=[0:1:(m-1)];
tm=tm';
plot(tm,in0','+',tm,yth(tm,xopt0),'-');
wstr1 = 'input of iir of ' + string(freqx) + 'Hz /' + '
theoretical analog gain' + string(db_fft1(1)) + ' dB' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
//
subplot(212);
plot(tm,out0','+',tm,yth(tm,xopt1),'-');
wstr1 = 'output of iir of ' + string(g0) + ' dB ' + string( ph0)
+ ' vs ' + ' theoretical digital gain' + string(db_fft2(1)) + '
dB' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
//
xset('window',wb0);
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function y = yth(t, x)
y = x(1) * sin( sin_delta * t + x(2))
//y = x(1) * sin( t + x(2))
endfunction
//--
// myfun(x0, tm, in0, wm)
// wm .* ( yth(tm, x0) - in0)
function e = myfun(x, tm, ym, wm)
e = wm .* ( yth(tm, x) - ym )
endfunction
//--
function [xopt]=sin_fit(wym)
// ym is samples
tm=[0:1:(m-1)];
tm=tm';
wm=ones(m,1);
// estimated function
// initial parameter
wz=abs(wym(1));
for v=1:m
if abs(wym(v)) > wz then
wz=abs(wym(v));
end
end
x0 = [ wz ; 0.0];
// 1- the simplest call
[f,xopt, gropt] = leastsq(list(myfun,tm,wym',wm),x0);
disp( xopt,'xopt');
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function save_para()
//
savefilename= input(' + enter file name for save parameters (ex:
para1.txt)',["string"]);
[fd0,err0]=mopen(savefilename,'w');
wstr1='/* ' + string(iiro2) + ' ORDER IIR DIGITAL
DE-EMPHASIS FILTER
COEFFICIENT */'
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='/* CONSTANT1 = ' + string(c50) +
'
*/'
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='/* CONSTANT2 = ' + string(c15) +
'
*/'
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='/* SAMPLING FREQUENCY = ' + string(fs) +
'
*/'
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
for v=1:iiro2
wstr1 = 'a[' + string(v) + ']=' + string( ac0(v)) ;
//mputstr(wstr1,fd0);
mfprintf(fd0,' %s;\n',wstr1);
end
wstr1 = 'b[0]=' + string( bcb0) ;
mfprintf(fd0,' %s;\n',wstr1);
for v=1:iiro2
wstr1 = 'b[' + string(v) + ']=' + string( bc0(v)) ;
//mputstr(wstr1,fd0);
mfprintf(fd0,' %s;\n',wstr1);
end
//mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
wstr1='/* An example of TYOKUSETU-GATA
2
*/';
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='/* in[i] is input, out[i] is
output
*/';
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='/* w[] are memory to keep stack old
data
*/';
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='/* initialize all w[1]=.....=0.0, and
then use it */';
mfprintf(fd0,'%s\n',wstr1);
for v=1:iiro2
wstr1= 'w[' + string(v) + '] = 0.0';
mfprintf(fd0,' %s;\n',wstr1);
end
mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
wstr1='for (i=0; i< number ; ++i) ';
mfprintf(fd0,' %s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='{';
mfprintf(fd0,' %s\n',wstr1);
wstr1='w[0] = in[i] + ';
for v=1:iiro2
wstr1= wstr1 + 'a[' + string(v) + '] * w[' + string(v) + ']';
if v < iiro2
wstr1= wstr1 + ' + ';
end
end
mfprintf(fd0,' %s;\n',wstr1);
wstr1='out[i] = ';
for v=0:iiro2
wstr1= wstr1 + 'b[' + string(v) + '] * w[' + string(v) + ']';
if v < iiro2
wstr1= wstr1 + ' + ';
end
end
mfprintf(fd0,' %s;\n',wstr1);
mfprintf(fd0,'\n');
for v=1:iiro2
wstr1= 'w[' + string(iiro2-v+1) +'] = w[' +
string(iiro2-v) + ']';
mfprintf(fd0,' %s;\n',wstr1);
end
wstr1='}';
mfprintf(fd0,' %s\n',wstr1);
//
err0=mclose([fd0]);
endfunction
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
impulse_steps=100;
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [ximpulse_steps]= set_synth2()
//
txt1=['steps (integral number)'];
wstr1=sprintf('%d',impulse_steps);
sig1=x_mdialog('impulse response based on do actual IIR
filter calculation',txt1, [wstr1 ]);
if sig1==[] then
arg1=evstr(wstr1);
else
arg1=evstr(sig1(1));
end
ximpulse_steps=arg1;
//
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [win0,wm]= make_impulse(ximpulse_steps)
//
win0=zeros(1,ximpulse_steps);
win0(1)=sin_level;
wm=ximpulse_steps;
//
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function plotimpulse(disp0)
wb0=xget('window'); // stack old window
xset('window',disp0); // create new windows
clf();
//
plot(out0);
wstr1 = 'impulse response ' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
//
xset('window',wb0);
endfunction
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function plotimpulse2(disp0,wdat1x)
wb0=xget('window'); // stack old window
xset('window',disp0); // create new windows
clf();
//
sz=size(wdat1x);
if sz(1,1)== 2 then
subplot(311);
plot(out0);
wstr1 = 'impulse response ' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
subplot(312);
win1=zeros(1,impulse_steps);
for v=1:impulse_steps
win1(1,v)=wdat1x(1,v);
end
plot(win1);
wstr1 = 'wdat ch1 ' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
subplot(313);
win1=zeros(1,impulse_steps);
for v=1:impulse_steps
win1(1,v)=wdat1x(2,v);
end
plot(win1);
wstr1 = 'wdat ch2 ' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
elseif sz(1,1) == 1 then
subplot(211);
plot(out0);
wstr1 = 'impulse response ' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
subplot(212);
win1=zeros(1,impulse_steps);
for v=1:impulse_steps
win1(1,v)=wdat1x(1,v);
end
plot(win1);
wstr1 = 'wdat ' ;
xtitle( wstr1 ,'','');
end
//
xset('window',wb0);
endfunction
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// .wav file process
//
//
// for .wav 1
chs1=0; // channels
qty1=0; // data quantity, samples
size1=0; // actual loaded data quantity
fs1=0; // sampling frequency
bit1=0; // bits
wavfile1=''; // file name, this will be overwritten.
wdat1=zeros(1,10);// data of the .wav, only one first channel,
this will be overwritten.
wdat2=zeros(1,10);// data of synthesized .wav, this will be
overwritten.
// for others
f412=0; // flag to detect scilab 4.1.2
defch1=1; // default channel 1
f_win=1; // flag if windows
//
// max stack size of input wave file
maxduration=30; // unit is second
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
if isdir('c:\\') then
f_win=1;
else
f_win=0;
end
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
function [xwdat1,wavfile1,chs1,qty1,fs1,bit1,f412]=get_wavfile_pro()
// choose wave file
wavfile1=tk_getfile(Title="Choose xxx.wav file name");
// read channels and samples
cs1=wavread(wavfile1,'size');
chs1=cs1(2); // channel
qty1=cs1(1); // samples
//...
if chs1 > 2 then // invert data for scilab-4.1.2
chs1=cs1(1);
qty1=cs1(2);
f412=1;
else
f412=0;
end
//...
sizeof0=8;
maxstacksize= 44100 * 2 * maxduration * sizeof0; // fs=44.1KHz 2
channels * maxduration seconds
if ( chs1 * qty1 * sizeof0 ) > maxstacksize then
qty1 = int((maxstacksize / (chs1 * sizeof0)));
disp('Waring: force to decrease data quantity(samples) ');
end
sz=stacksize();
if (sz(1)-sz(2)) < maxstacksize then
stacksize( (maxstacksize+sz(1)));
disp('increase stack memory ');
end
//
if f412 == 1 then // for windows scilab-4.1.2
[xwdat1,fs1,bit1]=wavread(wavfile1,[1,qty1]);
else
[xwdat1b,fs1,bit1]=wavread(wavfile1,[1,qty1]);
xwdat1=xwdat1b';
end
//
disp('read done');
endfunction
//----------------------------------------------------------------
function snd_play2(xwdat2)
// this sound doesnot work well on windows scilab-3.1.1 and linux
scilab-3.1
// but, this sound works on windows scilab-4.1.2. But, linux
scilab-4.1.2 doesnot!
//
sz=size(xwdat2);
size2=sz(2);
if f_win == 1 then
if f412 == 1 then // for windows scilab-4.1.2
sound(xwdat2 ,fs1,bit1);
else
// for windows scilab-3.1.1
disp('This function does not work.');
end
else // if f_win == 1 then
if f412 == 1 then // for scilab-4.1.2
disp('If sound setting is good for scilab, this function maybe
work.');
sound(xwdat2 ,fs1,bit1);
else
disp('This function does not work.');
end
end //if f_win == 1 then
endfunction
//
//----------------------------------------------------------------
function snd_save2( xwdat2)
wavefilename= input(' + enter file name for saved .wav file
=>',["string"]);
//
if f412 == 1 then // for windows scilab-4.1.2
wavwrite(xwdat2 ,fs1,bit1,wavefilename );
else
// for windows scilab-3.1.1
wavwrite(xwdat2',fs1,bit1, wavefilename);
end
endfunction
//
//----------------------------------------------------------------
// function display the .wav property
function disp_pro_wav()
disp(qty1,'data quantity',bit1,
'bits',chs1,'channels',fs1,'sampling frequency');
endfunction
//--------------------------------------
function [xwdat2]=do_iir_filtering(xwdat1)
sz=size(xwdat1);
xwdat2=zeros(sz(1),sz(2));
disp( sz(1),'channels ', sz(2),'data quantity ');
//
wk0=zeros(sz(1),iiro2);
//
for i=1:sz(2) // long
a=int( i / 44100);
b= i - 44100 * a;
if b == 0 then
disp( i );
end
for p=1:sz(1) // ch
w = xwdat1(p,i);
for v=1:iiro2
w= w + ac0(v) * wk0(p,v);
xwdat2(p,i)= xwdat2(p,i) + bc0(v) * wk0(p,v);
end
xwdat2(p,i) = xwdat2(p,i) + bcb0 * w;
for v=1:(iiro2-1)
wk0( p, iiro2 - v + 1) = wk0( p,iiro2 - v);
end
wk0(p,1)=w;
if xwdat2(p,i) > 1.0 then
xwdat2(p,i) =1.0;
elseif xwdat2(p,i) < -1.0 then
xwdat2(p,i)=-1.0;
end
end
end
//
disp('do iir filter done');
endfunction
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [xwdat2]=do_iir_filtering2(wH0, xwdat1)
sz=size(xwdat1);
disp( sz(1),'channels ', sz(2),'data quantity ');
//
//
if sz(1) == 2 then
sl=tf2ss([ wH0, 0; 0, wH0]);
disp('from transfer to state-space');
xwdat2=dsimul(sl,xwdat1);
elseif sz(1) == 1 then
sl=tf2ss(wH0);
disp('from transfer to state-space');
xwdat2=dsimul(sl,xwdat1);
else
disp('error: not define yet. ');
end
//
disp('do iir filter done');
endfunction
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [xwdat2]=do_iir_filtering3(wH0, xwdat1)
sz=size(xwdat1);
disp( sz(1),'channels ', sz(2),'data quantity ');
//
//
if sz(1) == 2 then
[H0r,H0nx]=syssize( wH0 ); // get size
viiro2=H0nx;
H0bunbo=denom( wH0 ); // get BUNBO
H0bunsi=numer( wH0 ); // get BUNSHI
vnum=[ H0bunsi,0; 0,H0bunsi];
vdenom=[ H0bunbo,0; 0,H0bunbo];
up=zeros(2,viiro2);
yp=zeros(2,viiro2);
xwdat2=rtitr(vnum,vdenom,xwdat1 ,up,yp);
elseif sz(1) == 1 then
[H0r,H0nx]=syssize( wH0 ); // get size
viiro2=H0nx;
H0bunbo=denom( wH0 ); // get BUNBO
H0bunsi=numer( wH0 ); // get BUNSHI
vnum= H0bunsi;
vdenom=H0bunbo;
up=zeros(1,viiro2);
yp=zeros(1,viiro2);
xwdat2=rtitr(vnum,vdenom,xwdat1 ,up,yp);
else
disp('error: not define yet. ');
end
//
disp('do iir filter done');
endfunction
//
//
//
//----------------------------------------------------------------
//===================================================================
//
// ++ MENU MENU MENU =====================
//
// Add menu buttons of which name are 'a_plotwav' and ''
//
ADD_MENU_PLOT=1; // set ADD_MENU 1
to add menu button of some functions
//
//
if ADD_MENU_PLOT == 1 then
delmenu('step1');
addmenu('step1',[ '(1)set_constant '; '(2)design IIR filter' ]);
step1=[ '[c50, c15, fs, iiro, c15_change]=set_constant()' ;' [H0,
S1A, iiro2]=filterdesign(); freq_response(0, 3, H0, S1A);'] ;
end //if ADD_MENU_PLOT == 1 then
//
//
//
ADD_MENU_KAISEI=1; // set ADD_MENU 1 to add menu button of
some functions
//
if ADD_MENU_KAISEI == 1 then
delmenu('step2');
addmenu('step2',[ '(1)system stable check '; '(2)gain by actual
IIR calculation' ]);
step2=[ '[iiro2]=system_stable_check(1, H0, S1A);' ; '[freqx, cyclex,
skip_cyclex]= set_synth(); [in0,sin_delta,m,sm]= make_sin(); [out0]=
cal_iir2(1); [in0,out0,m]=start_skip(); [xopt0]=sin_fit(in0);
[xopt1]=sin_fit(out0); plotfit(3);'] ;
end //if ADD_MENU_KAISEI == 1 then
//
//
//
ADD_MENU_SAVE=1; // set ADD_MENU 1 to add menu button of
some functions
//
if ADD_MENU_SAVE == 1 then
delmenu('step3');
addmenu('step3',[ '(1)save coefficient in a text file.' ]);
step3=[ 'save_para();'] ;
end //if ADD_MENU_SAVE == 1 then
//
//
//
ADD_MENU_IMPULSE=1; // set ADD_MENU 1 to add menu button of
some functions
//
if ADD_MENU_IMPULSE == 1 then
delmenu('step4');
addmenu('step4',[ '(1a)impulse response ', '(1b)impulse response
(state-space method)']);
step4=[ '[impulse_steps]= set_synth2(); [in0,m]=
make_impulse(impulse_steps); [out0]= cal_iir2(1); plotimpulse(4)';
'[impulse_steps]= set_synth2(); [in0,m]= make_impulse(impulse_steps);
[out0]= do_iir_filtering2(H0, in0); plotimpulse(4)' ] ;
end //if ADD_MENU_IMPULSE == 1 then
////
//
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
//
ADD_MENU_WAV=1; // set ADD_MENU 1
to add menu button of some functions
//
//
if ADD_MENU_WAV == 1 then
delmenu('step5');
addmenu('step5',[ '(1)read a .wav file (read only limited duration)',
'(2a)do IIR filtering (rtitr)' , '(2b)do IIR filtering (takes time)'
,'(3)play the wav filtered' , '(4)save as a .wav file' ]);
step5=[ 'wdat1=zeros(1,1); wdat2=zeros(1,1);
[wdat1,wavfile1,chs1,qty1,fs1,bit1,f412]=get_wavfile_pro();
disp_pro_wav(); ','[wdat2]=do_iir_filtering3(H0, wdat1);',
'[wdat2]=do_iir_filtering(wdat1);','snd_play2(wdat2);','snd_save2(
wdat2);'];
end //if ADD_MENU_WAV == 1 then
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
//
ADD_MENU_WAVIMPU=1; // set ADD_MENU
1 to add menu button of some functions
//
//
if ADD_MENU_WAVIMPU == 0 then
delmenu('step6');
addmenu('step6',[ '(1)a .wav with impulse response (state-space
method)', '(2)wav filtered with impulse response (state-space
method)']);
step6=[ '[impulse_steps]= set_synth2(); [in0,m]=
make_impulse(impulse_steps); [out0]= do_iir_filtering2(H0, in0);
plotimpulse2(4,wdat1)' ,'[impulse_steps]= set_synth2(); [in0,m]=
make_impulse(impulse_steps); [out0]= do_iir_filtering2(H0, in0);
plotimpulse2(4,wdat2)'] ;
end //if ADD_MENU_WAVIMPU == 1 then
ディエンファシスのIIRフィルターの係数を16ビットに変換して、16ビットかける16ビットが32ビットの
乗算機を使って計算したとき、周波数特性がどのようになるかを調べるため、後半にあるプログラムを使って、擬似的に100Hz,5000Hz,
16000Hzの利得を計算してみた。ここでは前提条件として、16
ビットのPCMデータを入力して、16ビットのデータを出力すること
を想定している。
周波数
|
標準値
|
振幅 327267 (0dB)
|
振幅 33(-60dB)
|
100Hz
|
-0.00389dB
|
-0.004dB
|
-0.33dB
|
5000Hz
|
-4.53dB
|
-4.51dB
|
-4.76dB
|
16000Hz
|
-9.04dB
|
-9.09dB
|
-9.67dB
|
ぼほフルスイングである振幅が32767で 振幅が大きなときは だいたい標準値が出ているが、約-60dB(1/1000)まで振幅が小さいと、怪しげ
な値になっている。
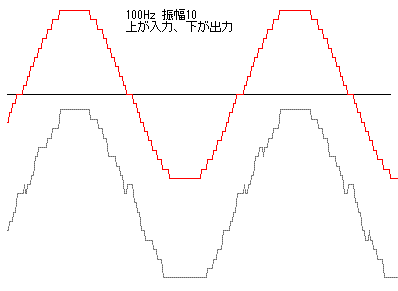
更に、振幅を小さくして10にしたときの波形を下図の示す。灰色の出力波形に入力にないぎざぎざが発生している。
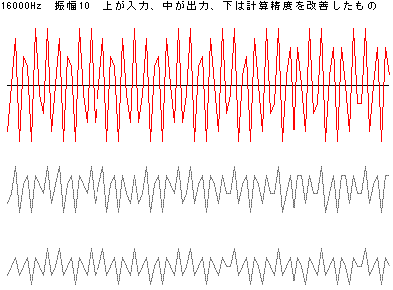
更に、減衰量がおおい16000Hzの波形を下図に示す。比較のため、浮動小数のdoubleで計算して最後に(short)で整数に変換して計算した出
力(計算精度を改善したもの)もこの図の一番下に加えてある。
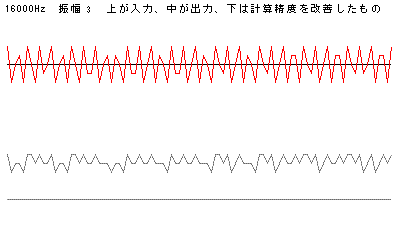
下図では、周波数16000Hzで入力の振幅が3であると、理論上の出力の振幅は
1.059(=3x0.353183(-3dB)となる。振幅3はSIN波のピークの値であって、サンプリングが荒いため入力の実質的な値は、0,1,2
をとることが多く、出力はほぼ零になる計算であるが、出力が零にならないことが分かる。
比較のための一番したの浮動小数のdoubleの出力(計算精度を改善したもの)は零になっているが、これは、最後に(short)を使って整数に変換す
るときに、たとえば、
(short)0.789523024567117 = 0
(short)-0.602814426388397 =0
と置き換えられてしまうためである。それに反して、下記では32bitから16bitの置き換えを切り捨てでおこなっているため、誤差は平均するとマイ
ナスの値で生じることになる。
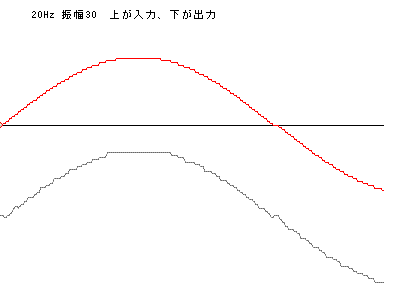
周波数が低いほど、入力の1周期分に対してのフィルターの演算量が多くなる。そこで、周波数の低い20Hzでの演算誤差の影響を見てみよう。下図は、周波
数20Hzの振幅30のSINを入力したときの出力の例である。出力の波形は滑らかではなく、ぎざぎざが生じている。 更に、周波数20Hzの振幅3の例では、まったく間違った値を出力している区間もある。
#define NCHANNEL2 2 /* チャンネル数 */
#define SHIFTx16 15 /*
data=(符号1ビット+データ15ビット) */
/* 係数16BIT 乗算機32BIT 版 */
void iir_deemphasis16(short *in0, short *out0, int init_flag,
unsigned long vol)
{
static long w[NCHANNEL2]; /* 前のデータを保持する記憶 */
long wout,wout2,w0;
int i;
/* de-emphasis IIR フィルターの係数 16bit換算の値。
32768=2^15が1に相当する。 */
short a1=20654; /* 0.6303142 * 2^15 */
short b0=15072; /* 0.4599584 * 2^15 */
short b1=-2958; /* -0.0902726 * 2^15 */
/* 前データが存在しないとき(例 初めての計算するときなど) wには零を入れる */
if ( init_flag == 1)
{
for (i=0;i<NCHANNEL2;++i) w[i] = 0;
}
for (i=0;i<NCHANNEL2;++i)
{
/* de-emphasis IIR フィルターの計算 */
w0= a1 * w[i];
w0 >>= SHIFTx16;
w0 += *(in0+i);
wout=b1 * w[i];
wout>>= SHIFTx16;
wout2= b0 * w0;
wout2 >>=SHIFTx16;
wout += wout2;
w[i]= w0;
/* ボリューム用の掛け算 */
/* 符号なし32bit整数のvolの値が32767以下ならば、volの値を乗算する */
/* vol=32768
が1倍に相当する。
*/
if (vol <= 32767 )
{
wout= wout * (long)vol;
wout >>=SHIFTx16;
}
/* 16bit の上限値と下限値の範囲になるようにする */
if (wout > 32767) wout=32767;
else if ( wout < -32768) wout=-32768;
*(out0+i)= (short)wout;
}
}
最後に、動作は保障できないが、もう少し精度のよいサンプルを示す。
係数は2の31乗をかけて、32bitの整数、
16bitの入力データは、2の12乗をかけて、28bitの整数に変換している。
ここでは、64bitの整数( __int64 または long long )が演算に使えると仮定している。
32bit x 28bit
は59bitになる(かりに ここでは 一番頭の1bitが符号を示すものとして考えている)。64bitの整数であるとオーバーフローに対してまだ
5bit分の余裕をもてる。但し、最後に、小数点のつじつまあわせに、1bit使ってしまうので、4bit分(=2の4乗は16)の余裕となるハズ、多
分。ディエンファシスフィルターの場合、利得が減衰する特性のフィルターなので出力も16bitを超えないと仮定すれば、IIRフィルターの計算の中で、
32bit x 28bit
の足し算は3回行われるので、2bit分(=2の2乗は4)あれば、オーバーフローがおきないことになる(定常出力の場合)。しかし、過渡的な応答の計算
の中では出力がどこまで大きくなるか分からないので、少し大きめに余裕をとってある。
まだ、28bitから 16bit
のデータに戻すときに、切り捨てでおこなっているので、あいかわらず誤差はよりマイナス側にでてくる。16bitのデータに戻す前に、小数点以下に適当な
値を加減算す
れば、見かけ上、誤差の平均を零として分散するようにできる かもしれない。
#define SHIFTx12 12 /* 28bit - 16bit */
#define NCHANNELS2 2 /* チャンネル数 */
/* 係数32BIT 乗算加算機32bit x 32(28)bit + 64(60)bit =
64(60)bit 途中計算28bit 版 */
void iir_deemphasis64(short *in0, short *out0, int init_flag)
{
static long w[2][NCHANNELS2]; /* 前のデータを保持する記憶
*/
long w0,x0,y0;
int i;
/* de-emphasis IIR フィルターの係数 32bit換算の値 */
long a1=1353589438; /* 0.6303142 * 2^31 */
long b0= 987753143; /* 0.4599584 * 2^31 */
long b1=-193858932; /* -0.0902726 * 2^31 */
/* 64bit 整数 __int64 叉は long long の有無 使い方は コンパイラーに依存する
! */
__int64 wout;
__int64 a64= 12345654321i64; /* 仮の意味のないデータをセット */
__int64 b64= 12345654321i64; /* 仮の意味のないデータをセット */
/* 前データが存在しないとき(例 初めての計算するときなど) wには零を入れる */
if ( init_flag == 1)
{
for (i=0;i<NCHANNELS2;++i) { w[0][i]
= 0; w[1][i] =0; }
}
for (i=0;i<NCHANNELS2;++i)
{
/* de-emphasis IIR フィルターの計算 */
x0=(long) *(in0+i);
/* 16bit から 28bit のデータにする */
x0 <<= SHIFTx12;
a64= b0;
b64= x0;
wout=a64 * b64; /* b0 * in; */
a64= b1;
b64= w[0][i];
wout += a64 * b64; /* b1 * w[0]; */
a64= a1;
b64= w[1][i];
wout += a64 * b64; /* a1 * w[1]; */
/*
上位32ビットを下位32ビットに移動し、32bitのy0に格納 */
wout >>= 32;
y0=(long)wout;
/* 小数点の調整 */
y0 <<=1;
/* 前データを格納 */
w[0][i]=x0;
w[1][i]=y0;
/* 28bitから 16bit のデータに戻す */
/* 右シフト演算であると 符号がマイナスのとき0が-1になってしまう対策 */
if (y0 < 0)
{
if (y0 > -4096)
y0=0;
else y0 >>= 12;
}
else y0 >>= 12;
/* 16bit の上限値と下限値の範囲になるようにする */
if (y0 > 32767) y0=32767;
else if ( y0 < -32768) y0=-32768;
*(out0+i)= (short)y0;
}
}
No.17b 2009年4月5日








