
A Study of Speech Recognition based on Inner Structure
by
Isi Shun
 |
A Study of Speech Recognition based on Inner Structure by
Isi Shun |
 |
A Study of Speech Recognition based on Inner Structure
< Preface >
This is a study of human process recognizing spoken phoneme .
Following idea is a hypothesis of speech recognition, which is
based on harmonic distortion.
To begin with, analyze spoken speech synchronizing with the pitch and calculate harmonic elements as measured feature, in order to get rid of dependency on voice fundamental frequency and also because distortion causes tone.
Sound source is distorted in mouth and is made into spoken speech.
In
general, sound source is not a simple SIN wave. So, suppose that sound
source consists of suitable simple harmonic. And estimate how to
distort,
calculate inversely from measurement harmonic elements to sound source
harmonic elements.
In this, suppose that the distortion is meaning of phoneme.
Telling about measurement and its processing for recognition, next subject is about discriminate-able.
One hypothesis, "Index should exist. The index has pervert view and treat various shape as limited form." is introduced to explain to be able to discriminate which one in various forms.
For instance, harmonic elements of japanese vowels utterance "AIUEO"
are calculated synchronizing with the pitch. And one distortion model
is
designed. Suppose that the distortion is identified by estimation
coefficient
of the distortion model.
Based on the coefficient (dimension is 23 in this example), principal
component analysis is done. Calculate main axes of which dispersion are
biggest and treat them as indices. And display the trace of the
utterance,
projecting the coefficients on the main axes.
Observation whether there is some difference for discrimination,
comparing
japanese vowel "A" portion of the trace with japanese vowel "O" portion
of the trace, is done.
Some languages, like chinese, changes of voice fundamental frequency are different meaning. In the future, distortion model should be developed to consider change of voice fundamental frequency.
This explanation is one experiment (a
hypothesis)
and it's not sure correct or not.
In order to discover the true
principle of pattern recognition, i
think, various experiments are
welcome.
1: Analysis of Harmonic Elements
| In speech recognition, some studies
based on
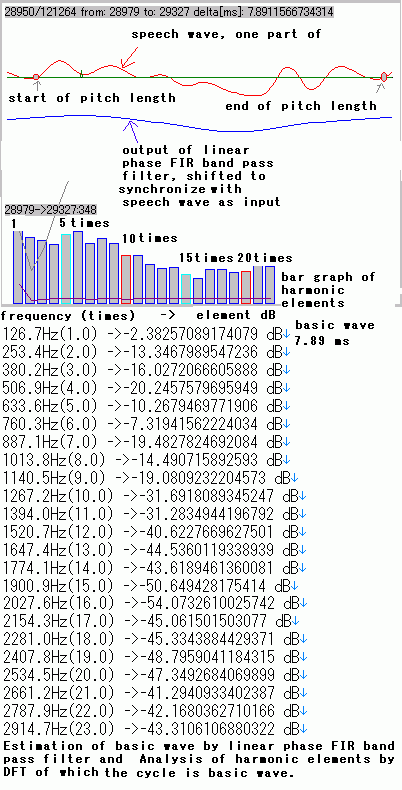
harmonic analysis were already done. In this study, the pitch (basic wave length) is indispensable information for recognition. And pitch is acquired by referring output from procedure of linear phase FIR (finite impulse response) band pass filter, because shifting input wave per linear phase delay can synchronize perfectly input wave and output of linear phase FIR band pass filter. Actually, for each person, basic wave length is different. So, prepare many band pass filters of which center frequency are different (filter bank) and select one to fit the person or the speech. The right figure is one portion of man speech wave, of which basic wave length is 7.89 ms. As basic wave length is fundamental, harmonic elements ,per dB unit, are gotten by DFT (discrete Fourier transform) calculation. Ordinary man's dynamic range of hearing is may more than 60 dB. In this sample, as measured feature, from 1 to 23 times harmonic is calculated. For every pitch part of speech wave, harmonic should be calculated like this. |
 |
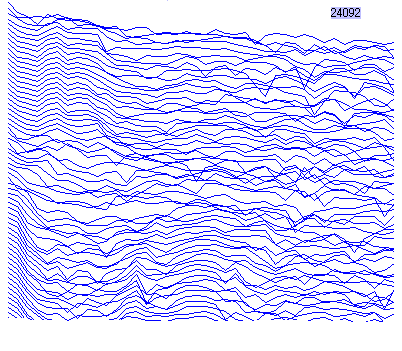
| The two plotted figures right shows
that 40 harmonic elements, arranged in time scale. In the figures,
values from left to right are one time
(fundamental) to 40 times harmonic element, and direction from
top to bottom is time passage. You see that there are strong correlation zone, weak correlation zone, and noisy zone (it does not matter so much whatever it is). It's important to discriminate them by carefully observation upon multi harmonic elements arranged in time scale. In above figure, in lower times harmonic, there is strong correlation, but in middle and high times harmonic, it may be noisy zone. And on the way, from some time, in middle times harmonic, strong correlation appears. In below figure, in middle times harmonic, there is weak correlation, as same time, strong correlation in lower times harmonic. Picking the leading part out of noise around may contribute more successful pattern recognition result. |
  |
i feel that, "Comparing based on the unit like cepstrum, spectrum, and
so on is not enough for speech signal pattern recognition. It needs to
analyze more detail, to detect what is controlled part of it and how to
be controlled on purpose, utilizing its change in stream of times. And
grasp close analysis will lead satisfactory answer.
And both speech recognition, and motion picture or image
recognition, maybe be done by same algorithm, after
appropriate signal processing."
2: Distortion Model of Sound Source
| Sound source is distorted in mouth and is made into spoken
speech. Phoneme
means the distortion. (This
is a hypothesis.) As one mathematical technique for describing how to distort, design some distortion model which has input and output, and estimate coefficient of the distortion model. Distortion itself is non-linear matter. In this, suppose that distortion can be described as transformation of harmonic elements. As one test, discrimination of phoneme by coefficient of distortion model is tried. |
 |
| True distortion model has not been decided yet. The design of distortion model is many potential. It should be developed in the future. |
| Always, opposite state or relative concept, is co-exist. That
is, somewhere
is "low" when it is "high". Also, somewhere is "cold" when it is "hot".
The state or concept like "high" and "hot" cannot exist without
opposite
one or relative one. In this, Simultaneous
Existence is defined as that concepts are discriminate-able
due to relative ones are co-exist. In general, Embodiments of one concept become various shape. It is infinite. How can we discriminate although there are so various shape ? So, let's think of the necessary condition to be discriminate-able. In this, as one hypothesis, the necessary condition is supposed that "Index should exist. The index has pervert view and treat various shape as limited form." For simplified instance, in japanese language, 5 main vowels, that are "A", "I","U","E",and"O" , are simultaneous existence. The border is rather continuous or mixed than distinct. Image that there is a space consisted from some (finite
number) indices
and each concept which is discriminated corresponds to sub-space of the
space. |
 |
| Indexes will be consisted of some
various measures, which detects different
feature. It may be well to think that
indexes are not combination of parameters based on
one
common measure, but combination of some various ones. Perhaps, index of the language (or the dialect) is different each other. As an example of french, almost japanese hear as one kind of vowel, although native french hear different vowel. Index should be tuned up to the language (or the dialect). |
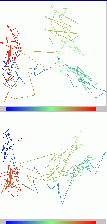
| To trial search for index, a
principal component analysis,
one major method of multivariate analysis, is done.
The right figure is the trace of japanese vowels utterance "AIUEO", projecting coefficients of a distortion model on the 1st axis 2nd axis plane and the 1st axis 3rd axis plane. For easy look on time dimension, the color degree of the trace line shows position on the track.. Color blue shows starting portion as utterance "A" and color red shows ending portion as utterance "O." In the 1st axis 3rd axis plane, it is showed that the
sub-space of "A"
and the sub-space of "O" is small different for discrimination. i do not think that the principal component analysis is good
solution for this issue. |
 |