次のページ
目次
その2: 3管声道モデルによる「お」の生成
のこころみ
2つの管(チューブ)をつなぎ合わせた模型による音声波形の生成のページでは、2つの管(チュー
ブ)のつなぎ合わせた
模型で生成できるのは 「あ」と「え」と
「う」の3つの音に限られると書いた。そこで、3つの管(チューブ)をつなぎ合わせれば、「お」の音を生成できるかどうかの実験をしてみた。
「お」の音は、「う」の発声に「あ」の放射特性が合体してできたイメージを考えた。
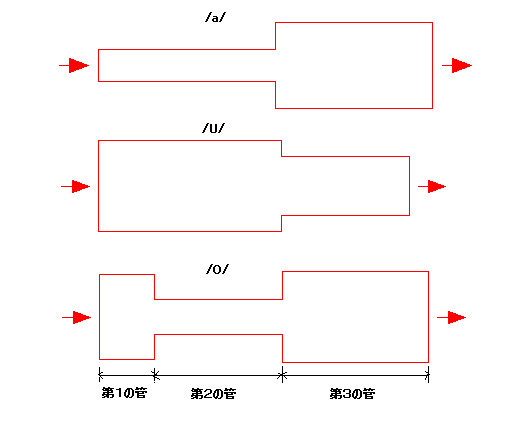
下図は、「あ」と「う」と「お」の音に何となく聞こえる、管のつなぎ
合わせのそれぞれの管の長
さと断面積をイメージしたものである。下図の一番下の絵が「お」のためのもので、「お」では3個の管が直列につなぎ合わさったもを使用する。入り口の左側
から なか にかけて
/U/の様に管が一段細くなっていて、なか から出口の右側にかけては/a/の様に少し長さを伴って一段開いたもになっている。参考に、これで生成した、「あ」
の音(発音記号の/a/)と、「う」
の音(発音記号の/U/)と、「お」
の音(発音記号の/O/)の.wavサンプルをリンクしておこう。
実際にいろいろな長さや断面積に設定して生成して音を聞いてみると、「お」に近い音に聞こえるようにするためには、予想以上に調整が必要なことがわかっ
た。
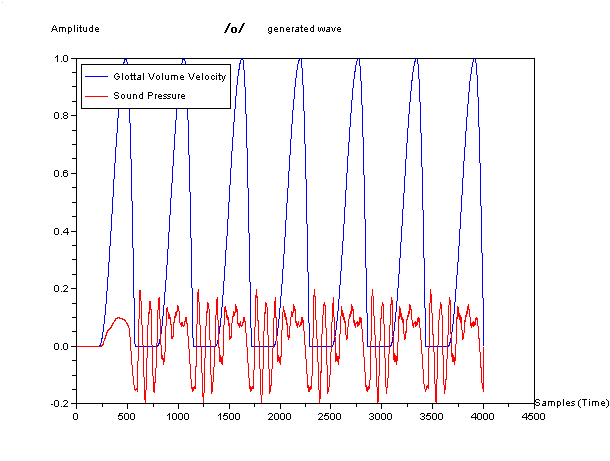
そして、下図が、この3つの管を直列につなぎ合わせた模型で生成した 何となく「お」の音に聞こえる波形の例である。青色が声門の波形を、赤色が音声に相
当する音圧の波形をしめしている。
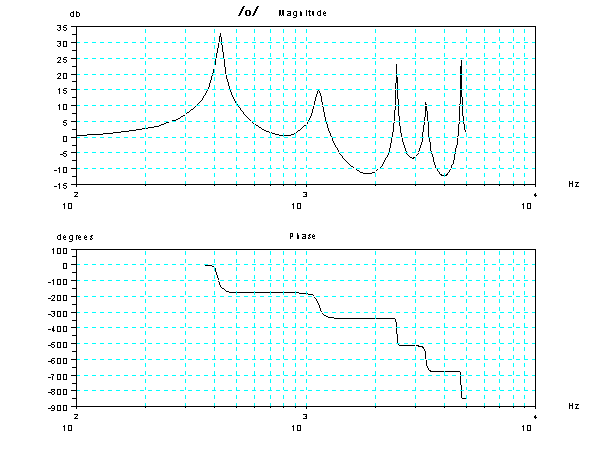
また 3つの管を直列につなぎ合わせた管の周波数と位相の特性(ボード線図)を参考(ご注意)
にのせておこう。
番外: 3
管声道モデルによる鼻音の生成
のこころみ
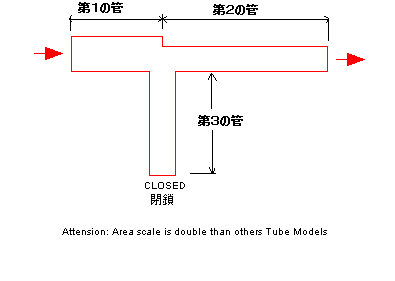
3つの管をつなぎあわせる方法は、もうひとつ、下図のように、Tの字につなぎあわせるものがある。このつなぎ方は鼻音の生成に相当する模型であるのでは
あ
るが、まだまだ不十分な結果しか得られていない。(補足説明)
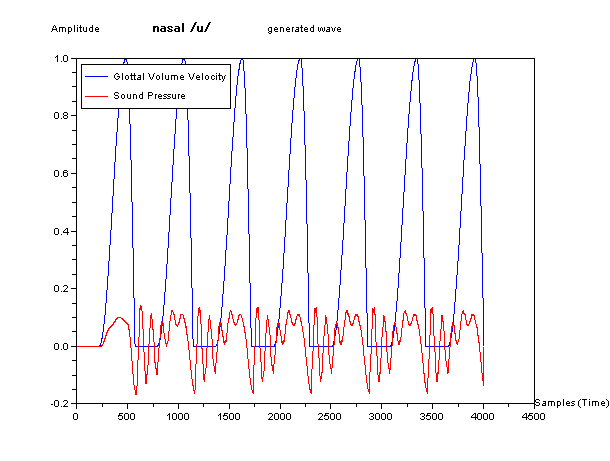
(「う」を鼻音風にしたつもりの .wav
サンプル まだまだ不十分な音) ここで言う鼻音とは、唇は閉じて鼻から音をだす、つまり、こもったような音である。おおざっぱに仕組みを言う
と、3つの管の中の一つ(下図では第3の管)の先を塞ぐ(閉じる)ことで、その管から入った音は先が塞がっているので外に出れないので また 反射して
入り口の方に戻ってくる。塞がった先まで行って反射してまた入り口まで戻ってくる時間と波形の位相の関係がちょうど入力の波形と逆になると、入力したもの
と反射し
たものが打ち消しあって、音が消音されるといった仕組みだ。
作画上の理由で、上図のTの字のつなぎあわせのイメージ図だけ、断面積の
尺度が他のものよりも大きくなって
いる。
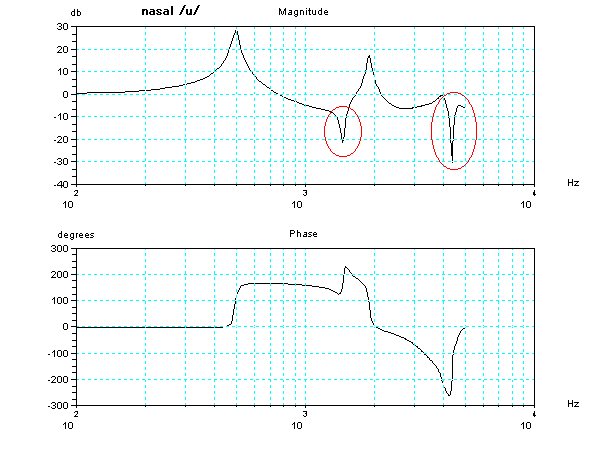
この3つの管をTの字につなぎ合わせた管の周波数と位相の特性(ボード線図)(ご
注意) をみると、下図の赤い丸でマークしたように、例えば周波数の10 3 (1000
Hz)の右側に、波形の大きさを示すdBの値が下に下がったがところがあることがわかる。
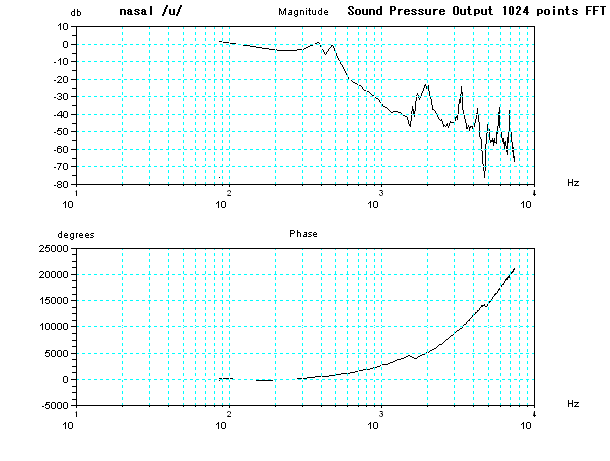
また、 生成した音圧の波形とそのFFTによる周波数分析の結果も参考にのせておこう。
また、フランス発の数値演算ライブラリ
SCILABを使って、この擬似的に人の音声のような波形を生成するサンプルプログラムを作ってみたので紹介しよう。
声門波形と2管声道モデルと3管声道モデルによる音声波形の生成のサンプルプログラム TubeModel46b.sciを以下に示す。
このサンプルを実際に動作させるためには、
ご使用されるプログラミング環境に合わせて修正・変更・追加などが必要かもしれません。
また、バグが含まれている可能性があります。
万一、このサンプルを動作させる場合は、あなたの責任でおこなってくださいね。
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract and Three Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
//
//
.........................................................................................
// PLEASE PAY ATTENSION that this program may have some bugs and also
you may modify program
// to fit your circumstances. If you use this program, everything done
by your own risk.
// Thanks.
//~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Physical Parameters (length and area) Setup
//
D_QTY=7;
// set dimension of list. This defines length of generated wave
// Generated wave's length will be around D_QTY * (N1+N2+N3).
T_QTY=3;
// T_QTY defines which Tubes Model is used.
// set T_QTY 2 or other than below values when Two Tubes
Model
// set T_QTY 3 when Three Tubes Model of serial type
// set T_QTY 4 when Three Tubes Model of "T" type
// sample length & area for /a/ from problems 3.8 in Digital
Processing of Speech Signals by L.R.Rabiner and R.W.Schafer
// set T_QTY=2 and use Two Tubes Model
//L1=[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9]; // set list of 1st
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A1=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]; // set list
of 1st tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
//L2=[8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8]; // set list of 2nd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A2=[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]; // set list
of 2nd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
// sample length & area for /ae/ from problems 3.8 in Digital
Processing of Speech Signals by L.R.Rabiner and R.W.Schafer
// set T_QTY=2 Two Tubes Model
//L1=[4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4]; // set list of 1st
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A1=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]; // set list
of 1st tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
//L2=[13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13, 13]; // set list
of 2nd tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A2=[8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8]; // set list
of 2nd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
// sample length & area for /i/ from problems 3.8 in Digital
Processing of Speech Signals by L.R.Rabiner and R.W.Schafer
// set T_QTY=2 and use Two Tubes Model
//L1=[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9]; // set list of 1st
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A1=[8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8]; // set list
of 1st tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
//L2=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]; // set list of 2nd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A2=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]; // set list
of 2nd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
// sample for /u/
// set T_QTY=2 and use Two Tubes Model
//L1=[10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10]; // set list
of 1st tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A1=[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]; // set list
of 1st tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
//L2=[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]; // set list of 2nd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A2=[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]; // set list
of 2nd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
// sample length & area for /o/ modoki
// set T_QTY=3 and use Three Tubes Model of serial type
L1=[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]; // set list of 1st
tube's length by unit is [cm]
A1=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]; // set list of
1st tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
L2=[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]; // set list of 2nd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
A2=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]; // set list of
2nd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
L3=[8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8]; // set list of 3rd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
A3=[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]; // set list of
3rd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
// sample for nasal /u/ This is not enough for nasal
sound effect.
// set T_QTY=4 and use Three Tubes Model of "T" type
//L1=[5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5]; // set list of 1st
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A1=[4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4]; // set list
of 1st tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
//L2=[9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9]; // set list of 2nd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A2=[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]; // set list
of 2nd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
//L3=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]; // set list of 3rd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
//A3=[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]; // set list
of 3rd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
c0=35000; // constant. the speed of sound is round
35000 cm/second
if T_QTY == 3 then //Three Tubes Model of serial type
tu1=L1./c0; // delay time in 1st tube
tu2=L2./c0; // delay time in 2nd tube
tu3=L3./c0; // delay time in 3rd tube
r1=(A2-A1)./(A2+A1); // reflection coefficient between 1st
tube and 2nd tube
r2=(A3-A2)./(A3+A2); // reflection coefficient between 2nd
tube and 3rd tube
elseif T_QTY == 4 then //Three Tubes Model of T type
tu1=L1./c0; // delay time in 1st tube
tu2=L2./c0; // delay time in 2nd tube
tu3=L3./c0; // delay time in 3rd tube
r12=((A2+A3)-A1)./(A3+A2+A1); // reflection coefficient
between 1st tube and others
r21=(A2-(A1+A3))./(A3+A2+A1); // reflection coefficient
between 2nd tube and others
r31=(A3-(A1+A2))./(A3+A2+A1); // reflection coefficient
between 3rd tube and others
else
//Two Tubes Model
tu1=L1./c0; // delay time in 1st tube
tu2=L2./c0; // delay time in 2nd tube
r1=(A2-A1)./(A2+A1); // reflection coefficient between 1st
tube and 2nd tube
end
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Input Glottal Volume Velocity for Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
// A.E.Rosenberg's formula as Glottal Volume Velocity
// Physical Parameters (duration) Setup
//
//D_QTY // set
dimension of list. This defines length of generated wave
tclosed=[5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5] ; // set
glottis closed duration (off time) by unit is millisecond [ms]
trise= [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]; // set
glottis opening duration (rise time) by unit is millisecond [ms]
tfall= [2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]; // set glottis closing duration
(fall time) by unit is millisecond [ms]
// below (tfall is smaller) is for /i/ that needs higher
frequency signals as input
//tclosed=[4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4] ; // set
glottis closed duration (off time) by unit is millisecond [ms]
//trise= [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]; // set
glottis opening duration (rise time) by unit is millisecond [ms]
//tfall= [0.7, 0.7, 0.7, 0.7, 0.7, 0.7, 0.7]; // set glottis
closing duration (fall time) by unit is millisecond [ms]
amplitude=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]; // set value of multiplier
// reflection coefficient between glottis and 1st tube
rg_rise=0.9; // set some value (1. or less)
when glottis is opening
rg_fall=0.95; // set some value (1. or less) when
glottis is closing
rg_closed=1; // When glottis is closed,
// reflection coefficient between glottis and 1st tube is 1
// because glottis's gate is closed and vocal tract is free from
glottis's influence
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Output Sound Pressure for Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
// Convert from Volume Velocity to Sound Pressure using High Pass
Filter Model for Mouth Radiation
// Parameters ( cut off frequecny ) Setup
//
fc=1000; // set cut off frequency of High Pass Filter by
unit is [Hz]
fnew=fc;
// reflection coefficient between 2nd tube and mouth
rl=0.9; // set adjust reduction response. rl is variable,
however use one constant in this.
// reflection coefficient of 3rd tube's terminal side. 3rd tube is
supposed that one side is closed.
// This parameter is used only when T_QTY is set to 4 as Three
Tubes Model of "T" type
rl3=-0.97; // set certain a value, beside ideal value is -1
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Other preparation: Sampling Frequency Setup
//
fs=44100; // set sampling frequency by unit is [Hz]
ts=1/fs;
//
Max_Freq=7500; // set plot maximum frequency by unit is [Hz]
//
//==========================================================================
//
// Step 1 Input Glottal Volume Velocity Generation
//
mess1='+++enter step 1 Input Glottal Volume Velocity Generation';
mess1
// length0 is wave length
length0=0;
N1= zeros(1, D_QTY);
N2= zeros(1, D_QTY);
N3= zeros(1, D_QTY);
for loop=1:D_QTY
N1(loop)= int( tclosed(loop) / 1000 / ts );
N2(loop)= int( trise(loop) / 1000 / ts);
N3(loop)= int( tfall(loop) / 1000 / ts);
LL(loop)= N1(loop)+N2(loop)+N3(loop);
length0 = length0 + LL(loop);
end
// yg is Glottal Volume Velocity. rg is reflection coefficient
between glottis and 1st tube
yg= zeros(1,length0+1);
rg= zeros(1,length0+1);
tc0=1;
yg(tc0)=0.;
yg(tc0)=amplitude(1) * yg(tc0);
for loop=1:D_QTY
for t0=1:int(LL(loop))
tc0=tc0+1;
if t0 < N1(loop) then
yg(tc0) =0;
rg(tc0)=rg_closed;
elseif t0 <= (N2(loop) + N1(loop)) then
yg(tc0)= 0.5 * ( 1 - cos( ( %pi / N2(loop) ) * (t0 -
N1(loop)) ) );
rg(tc0)=rg_rise;
elseif t0 <= (N3(loop)+N2(loop)+N1(loop)) then
yg(tc0)= cos( ( %pi / ( 2 * N3(loop) )) * ( t0 -
(N2(loop)+N1(loop)) ) );
rg(tc0)=rg_fall;
else
yg(tc0) =0;
rg(tc0)=rg_closed;
end
yg(tc0)=amplitude(loop) * yg(tc0);
end // t0
end // loop
// function save yg (Glottal Volume Velocity) as one sound wave file
function save_as_sound_file_yg( filename)
max01=0.;
for loop=1:length0
if abs( yg(loop) ) > max01 then
max01 = abs( yg(loop));
end
end
y3out2=zeros(1,length0+1)';
if max01 > 0. then
for loop=1:length0
y3out2(loop)= yg(loop) / max01;
end
end
wavwrite(y3out2, fs, 16, filename );
endfunction
// Function for yg (Glottal Volume Velocity) frequency-phase response
function yg_bode(ni)
frq=[100:25:Max_Freq];
frqs=size(frq);
resp=zeros(1,frqs(2));
stp=0;
if ni > 1 then
for v=1:(ni-1)
stp=stp + LL(v);
end
end
stp=stp+N1(ni);
y00=0.;
for v=1:(N2(ni)+N3(ni)+1)
y00= y00 + yg(stp + v);
end
for w=1:frqs(2)
xw=2 * %pi * frq(w) * ts;
yi=0;
for v=1:(N2(ni)+N3(ni)+1)
yi= yi + yg(stp + v) * %e^(-1. * xw * (v-1) * %i);
end // for v
resp(w)=yi / y00;
end // for w
[db,phi] =dbphi(resp);
clf();
bode(frq,db,phi);
endfunction
//
// End of Step 1 Input Glottal Volume Velocity Generation
//
//==========================================================================
//
// Step 2 Three Tubes/Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
Calculation
//
if T_QTY == 3 then //Three Tubes Model of serial type
mess2='+++enter step 2 Three Tubes Model of serial type for
Vocal Tract Calculation';
mess2
// yt is output of Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
M1= zeros(1, D_QTY);
M2= zeros(1, D_QTY);
M3= zeros(1, D_QTY);
y2tm= zeros(1,length0+1);
for loop=1:D_QTY
M1(loop)= int( tu1(loop) / ts ) + 1;
M2(loop)= int( tu2(loop) / ts ) + 1;
M3(loop)= int( tu3(loop) / ts ) + 1;
end
MAX_M1=M1(1);
MAX_M2=M2(1);
MAX_M3=M3(1);
for loop=1:D_QTY
if M1(loop) > MAX_M1 then
MAX_M1= M1(loop)
end
if M2(loop) > MAX_M2 then
MAX_M2= M2(loop)
end
if M3(loop) > MAX_M3 then
MAX_M3= M3(loop)
end
end
ya1= zeros(1,MAX_M1);
ya2= zeros(1,MAX_M1);
yb1= zeros(1,MAX_M2);
yb2= zeros(1,MAX_M2);
yc1= zeros(1,MAX_M3);
yc2= zeros(1,MAX_M3);
tc0=1;
ya1(tc0)=0.;
ya2(tc0)=0.;
yb1(tc0)=0.;
yb2(tc0)=0.;
yc1(tc0)=0.;
yc2(tc0)=0.;
y2tm(tc0)=0.;
for loop=1:D_QTY
for t0=1:int(LL(loop))
tc0=tc0+1;
for jl=MAX_M1:-1:2
ya1(jl)=ya1(jl-1);
ya2(jl)=ya2(jl-1);
end
for jl=MAX_M2:-1:2
yb1(jl)=yb1(jl-1);
yb2(jl)=yb2(jl-1);
end
for jl=MAX_M3:-1:2
yc1(jl)=yc1(jl-1);
yc2(jl)=yc2(jl-1);
end
ya1(1)= ((1. + rg(tc0) ) / 2.) * yg(tc0) + rg(tc0) *
ya2(M1(loop));
ya2(1)= -1. * r1(loop) * ya1(M1(loop)) + ( 1. -
r1(loop) ) * yb2(M2(loop));
yb1(1)= ( 1 + r1(loop) ) * ya1(M1(loop)) + r1(loop) *
yb2(M2(loop));
yb2(1)= -1. * r2(loop) * yb1(M2(loop)) + ( 1. -
r2(loop) ) * yc2(M3(loop));
yc1(1)= ( 1 + r2(loop) ) * yb1(M2(loop)) + r2(loop) *
yc2(M3(loop));
yc2(1)= -1. * rl * yc1(M3(loop));
y2tm(tc0)= (1 + rl) * yc1(M3(loop));
end // t0
end //loop
elseif T_QTY == 4 then //Three Tubes Model of T type
mess2='+++enter step 2 Three Tubes Model of T type for
Vocal Tract Calculation';
mess2
// yt is output of Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
M1= zeros(1, D_QTY);
M2= zeros(1, D_QTY);
M3= zeros(1, D_QTY);
y2tm= zeros(1,length0+1);
for loop=1:D_QTY
M1(loop)= int( tu1(loop) / ts ) + 1;
M2(loop)= int( tu2(loop) / ts ) + 1;
M3(loop)= int( tu3(loop) / ts ) + 1;
end
MAX_M1=M1(1);
MAX_M2=M2(1);
MAX_M3=M3(1);
for loop=1:D_QTY
if M1(loop) > MAX_M1 then
MAX_M1= M1(loop)
end
if M2(loop) > MAX_M2 then
MAX_M2= M2(loop)
end
if M3(loop) > MAX_M3 then
MAX_M3= M3(loop)
end
end
ya1= zeros(1,MAX_M1);
ya2= zeros(1,MAX_M1);
yb1= zeros(1,MAX_M2);
yb2= zeros(1,MAX_M2);
yc1= zeros(1,MAX_M3);
yc2= zeros(1,MAX_M3);
tc0=1;
ya1(tc0)=0.;
ya2(tc0)=0.;
yb1(tc0)=0.;
yb2(tc0)=0.;
yc1(tc0)=0.;
yc2(tc0)=0.;
y2tm(tc0)=0.;
for loop=1:D_QTY
for t0=1:int(LL(loop))
tc0=tc0+1;
for jl=MAX_M1:-1:2
ya1(jl)=ya1(jl-1);
ya2(jl)=ya2(jl-1);
end
for jl=MAX_M2:-1:2
yb1(jl)=yb1(jl-1);
yb2(jl)=yb2(jl-1);
end
for jl=MAX_M3:-1:2
yc1(jl)=yc1(jl-1);
yc2(jl)=yc2(jl-1);
end
ya1(1)= ((1. + rg(tc0) ) / 2.) * yg(tc0) + rg(tc0) *
ya2(M1(loop));
ya2(1)= -1. * r12(loop) * ya1(M1(loop)) + ( 1. -
r12(loop) ) * yb2(M2(loop)) + ( 1. - r12(loop)) * yc2(M3(loop));
yb1(1)= ( 1 + r21(loop) ) * ya1(M1(loop)) + r21(loop) *
yb2(M2(loop)) + ( 1. + r21(loop)) * yc2(M3(loop));
yb2(1)= -1. * rl * yb1(M2(loop));
y2tm(tc0)= (1 + rl) * yb1(M2(loop));
yc1(1)= ( 1. + r31(loop) ) * ya1(M1(loop)) + r31(loop) *
yc2(M3(loop)) + ( 1. + r31(loop) ) * yb2(M2(loop)) ;
yc2(1)= -1. * rl3 * yc1(M3(loop));
end // t0
end //loop
else //Two Tubes Model
mess2='+++enter step 2 Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
Calculation';
mess2
// yt is output of Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract
M1= zeros(1, D_QTY);
M2= zeros(1, D_QTY);
y2tm= zeros(1,length0+1);
for loop=1:D_QTY
M1(loop)= int( tu1(loop) / ts ) + 1;
M2(loop)= int( tu2(loop) / ts ) + 1;
end
MAX_M1=M1(1);
MAX_M2=M2(1);
for loop=1:D_QTY
if M1(loop) > MAX_M1 then
MAX_M1= M1(loop)
end
if M2(loop) > MAX_M2 then
MAX_M2= M2(loop)
end
end
ya1= zeros(1,MAX_M1);
ya2= zeros(1,MAX_M1);
yb1= zeros(1,MAX_M2);
yb2= zeros(1,MAX_M2);
tc0=1;
ya1(tc0)=0.;
ya2(tc0)=0.;
yb1(tc0)=0.;
yb2(tc0)=0.;
y2tm(tc0)=0.;
for loop=1:D_QTY
for t0=1:int(LL(loop))
tc0=tc0+1;
for jl=MAX_M1:-1:2
ya1(jl)=ya1(jl-1);
ya2(jl)=ya2(jl-1);
end
for jl=MAX_M2:-1:2
yb1(jl)=yb1(jl-1);
yb2(jl)=yb2(jl-1);
end
ya1(1)= ((1. + rg(tc0) ) / 2.) * yg(tc0) + rg(tc0) *
ya2(M1(loop));
ya2(1)= -1. * r1(loop) * ya1(M1(loop)) + ( 1. -
r1(loop) ) * yb2(M2(loop));
yb1(1)= ( 1 + r1(loop) ) * ya1(M1(loop)) + r1(loop) *
yb2(M2(loop));
yb2(1)= -1. * rl * yb1(M2(loop));
y2tm(tc0)= (1 + rl) * yb1(M2(loop));
end // t0
end //loop
end //End of Two Tubes model
// Function for disply two tubes model's frequency-phase response when
glottis is closed
function y = two_tubes( xw, ni, rg0, rl0 )
yi = 0.5 * ( 1 + rg0 ) * ( 1 + r1(ni)) * ( 1 + rl0 )
* %e^( -1 * ( tu1(ni) + tu2(ni) ) .* xw * %i);
yb = 1 + r1(ni) * rg0 * %e^( -2 * tu1(ni) .* xw * %i) +
r1(ni) * rl0 * %e^( -2 * tu2(ni) .* xw * %i) + rl0 * rg0 * %e^( -2 *
(tu1(ni) + tu2(ni)) .* xw * %i);
y = yi ./ yb;
endfunction
function two_tubes_model_bode(ni)
frq=[100:25:Max_Freq]';
[db,phi] =dbphi(two_tubes(2 * %pi * frq, ni,rg_closed ,rl));
clf();
bode(frq,db,phi);
endfunction
// Function for disply three tubes model's frequency-phase response
when glottis is closed
function y = three_tubes( xw, ni, rg0, rl0 )
if T_QTY == 4 then // "T" type
yi = 0.5 * ( 1. + rg0 ) * ( 1. + r21(ni)) * ( 1. +
rl0 ) * %e^( -1. * ( tu1(ni) + tu2(ni)) * xw * %i);
yb = 1.0;
yb = yb + r12(ni) * rg0 * %e^( -2 * tu1(ni) * xw * %i) +
r21(ni) * rl0 * %e^( -2 * tu2(ni) * xw * %i);
yb = yb + rg0 * rl0 * ( 1. - r12(ni) + r21(ni) ) * %e^( -2
* (tu1(ni) + tu2(ni)) * xw * %i);
yc = rl3 * ( 1. + r31(ni));
yc = yc * (1. + rg0 * %e^( -2 * tu1(ni) * xw * %i));
yc = yc * (1. - rl0 * %e^( -2 * tu2(ni) * xw * %i));
yc = yc * %e^( -1 * tu3(ni) * xw * %i);
yd = 1. - rl3 * %e^( -2 * tu3(ni) * xw * %i);
if yd == 0. then // There is room for
reconsideration in this limit value.
y=0.; // because yc/yd is infinity when yd = 0
else
yc = yc / yd;
y = yi / ( yb + yc);
end
else // serial type
yi = 0.5 * ( 1. + rg0 ) * ( 1. + r1(ni)) * ( 1. + r2(ni)) *
( 1. + rl0 ) * %e^( -1. * ( tu1(ni) + tu2(ni) + tu3(ni)) * xw *
%i);
yb = 1 + rg0 * r1(ni) * %e^( -2 * tu1(ni) * xw * %i) +
r1(ni) * r2(ni) * %e^( -2 * tu2(ni) * xw * %i) + r2(ni) * rl0 * %e^( -2
* tu3(ni) * xw * %i);
yb = yb + rg0 * r2(ni) * %e^( -2 * (tu1(ni) + tu2(ni)) * xw * %i)
+ r1(ni) * rl0 * %e^( -2 * (tu2(ni) + tu3(ni)) * xw * %i);
yb = yb + rg0 * r1(ni) * r2(ni) * rl0 * %e^( -2 * (tu1(ni)
+ tu3(ni)) * xw * %i);
yb = yb + rg0 * rl0 * %e^( -2 * (tu1(ni) + tu2(ni) +
tu3(ni)) * xw * %i);
y = yi / yb;
end
endfunction
function three_tubes_model_bode(ni)
frq3=[100:25:Max_Freq];
frq3s=size(frq3);
resp3=zeros(1,frq3s(2));
for v=1:frq3s(2)
resp3(v)= three_tubes(2 * %pi * frq3(v), ni,rg_closed ,rl);
end
[db,phi] =dbphi(resp3);
clf();
bode(frq3,db,phi);
endfunction
// Function plot sqrt(area) vs length
function plot_area(ni)
clf();
plot2d(0,0,1,"010","",[-5,-10,20,10],[5,5,4,5]); // wake wo egaku
if T_QTY == 4 then //Three Tubes Model of T type
ya1=sqrt(A1(ni) );
ya2=sqrt(A2(ni) );
ya3=sqrt(A3(ni) );
if ya2 > ya1 then
yy0=ya2;
else
yy0=ya1;
end
yy0=10- (yy0 * 2);
// Area scale is double than other Tube Models.
yy1=ya1 + yy0;
yy2=ya2 + yy0;
yy3=yy0 - L3(ni);
xx1=L1(ni) - (ya3 / 2);
xx2=L1(ni) + (ya3 / 2);
xp=[0 0 xx1 xx1
xx2 xx2 L1(ni)+L2(ni) L1(ni)+L2(ni)
L1(ni) L1(ni) 0 ]';
yp=[yy1 yy0 yy0 yy3 yy3
yy0
yy0
yy2
yy2 yy1 yy1]';
xpolys( xp, yp, [5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5] );
xar=[-2 -0.5];
yar=[yy0+ ( ya1 / 2 ) yy0+ ( ya1 / 2 ) ];
xarrows(xar, yar, 1, 5);
yar=[yy0 + ( ya2 / 2 ) yy0+ ( ya2 / 2 ) ];
xar=[ L1(ni)+L2(ni)+0.5 L1(ni)+L2(ni)+2];
xarrows(xar, yar, 1, 5);
xstring(xx1, yy3 - 1, "CLOSED");
xstring(0,-9,"Attension: Area scale is double than others Tube Models");
//
elseif T_QTY == 3 then //Three Tubes Model of serial type
ya1=sqrt(A1(ni) );
ya2=sqrt(A2(ni) );
ya3=sqrt(A3(ni) );
xp=[0 0 L1(ni) L1(ni)
L1(ni)+L2(ni) L1(ni)+L2(ni) L1(ni)+L2(ni)+L3(ni) L1(ni)+L2(ni)+L3(ni)
L1(ni)+L2(ni) L1(ni)+L2(ni) L1(ni) L1(ni) 0 ]';
yp=[ya1 -ya1 -ya1
-ya2
-ya2
-ya3
-ya3
ya3
ya3
ya2
ya2 ya1 ya1 ]';
xpolys( xp, yp, [5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5] );
xar=[-2 -0.5];
yar=[0 0];
xarrows(xar, yar, 1, 5);
xar=[ L1(ni)+L2(ni)+L3(ni)+0.5 L1(ni)+L2(ni)+L3(ni)+2];
xarrows(xar, yar, 1, 5);
else //Two Tubes Model
ya1=sqrt(A1(ni) );
ya2=sqrt(A2(ni) );
xp=[0 0 L1(ni)
L1(ni) L1(ni)+L2(ni) L1(ni)+L2(ni)
L1(ni) L1(ni) 0 ]';
yp=[ya1 -ya1 -ya1
-ya2
-ya2
ya2
ya2 ya1 ya1 ]';
xpolys( xp, yp, [5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5] );
xar=[-2 -0.5];
yar=[0 0];
xarrows(xar, yar, 1, 5);
xar=[ L1(ni)+L2(ni)+0.5 L1(ni)+L2(ni)+2];
xarrows(xar, yar, 1, 5);
end
endfunction
//
// End of Step 2 Two Tubes Model for Vocal Tract Calculation
//
//==========================================================================
//
// Step 3 Output Sound Pressure for Two Tubes Model for
Vocal Tract Calculation
//
mess3='+++enter step 3 Output Sound Pressure for Two Tubes Model
for Vocal Tract Calculation';
mess3
// At first, low pass filter's coefficients
wc=2. * %pi * fc;
al1= -1. * %e^( -1. * wc * ts);
bl0= wc * ts;
// Then, convert them to high pass filter's coefficients
function y=f_alfa( wc_org, wc_new)
y= -1. * cos( (wc_org + wc_new) * ts /2. ) / cos( (wc_org -
wc_new) * ts / 2. );
endfunction
wnew=2. * %pi * fnew;
alfa=f_alfa( wc, wnew );
// high pass filter's coefficients
bh0= bl0 / (1.0 - al1 * alfa);
bh1= alfa * bl0 / (1.0 - al1 * alfa);
ah1= (alfa - al1) / (1.0 - al1 * alfa);
// IIR type high pass filter
y3out= zeros(1,length0+1);
LI1=2;
LI2=2;
ya1= zeros(1,LI1);
yb1= zeros(1,LI2);
//loop
for loop=1:length0
ya1(LI1)=ya1(1);
yb1(LI2)=yb1(1);
ya1(1)=y2tm(loop);
yb1(1)= bh0 * ya1(1) + bh1 * ya1(LI1) - ah1 * yb1(LI2);
y3out(loop)=yb1(1);
end //loop
// Function for disply high pass filter's frequency-phase response
function y = hpf1( xw )
yi= bh0 + bh1 * cos( xw * ts) - bh1 * sin( xw * ts ) * %i;
yb=1.0 + ah1 * cos( xw * ts ) - ah1 * sin( xw *
ts ) * %i;
y=yi ./yb;
endfunction
function hpf_bode()
frq=[100:25:Max_Freq]';
[db,phi] =dbphi(hpf1(2 * %pi * frq ));
clf();
bode(frq,db,phi);
endfunction
// function save y3out (Sound Pressure) as one sound wave file
function save_as_sound_file( filename)
max01=0.;
for loop=1:length0
if abs( y3out(loop) ) > max01 then
max01 = abs( y3out(loop));
end
end
y3out2=zeros(1,length0+1)';
if max01 > 0. then
for loop=1:length0
y3out2(loop)= y3out(loop) / max01;
end
end
wavwrite(y3out2, fs, 16, filename );
endfunction
//
//
// End of Step 3 Output Sound Pressure for Two Tubes Model
for Vocal Tract
//
//================================================================================
//
// Step 4 Plot Glottal Volume Velocity and Sound Pressure
//
mess4='+++enter step 4 Plot generated sound wave';
mess4
function plot_yg_yout()
clf();
plot(yg,'b');
plot(y3out,'r');
xtitle('generated wave','Samples (Time)', 'Amplitude');
legend('Glottal Volume Velocity','Sound Pressure',2);
endfunction
plot_yg_yout();
// Function FFT y3out(Sound Pressure) and plot frequency-phase
// FFT starts from 2nd section
// input argument lng is fft points 1024 or others
// points 1024, when nzyou=10
// points 2048, when nzyou=11
// points 4096, when nzyou=12
function ntz=fft_plot( lng )
nzyou= int(log2( lng ));
ntz=2^nzyou;
// check if data length is enough for fft
ct0=0;
for loop=2:D_QTY
ct0=ct0+LL(loop);
end
if ct0 > ntz then // when actual data > ntz
xin1=zeros(1,ntz);
ofs=LL(1); // FFT starts from 2nd section
for loop=1:ntz
xin1(loop) = y3out( loop + ofs);
end
win_hn=window('hn',ntz); // make hanning windows data
xin2= xin1 .* win_hn;
fftout=fft(xin2,-1);
dfs= fs / ntz;
p100= int(100. / dfs);
p10000= int(Max_Freq / dfs);
frq=[(dfs * p100):dfs:(dfs * p10000)];
frqs=size(frq);
resp=zeros(1,frqs(2));
ct0=1;
for loop=p100:p10000
resp(ct0)=fftout( loop + 1) / fftout(1);
ct0=ct0+1;
end
[db,phi] =dbphi(resp);
clf();
bode(frq,db,phi);
end // when actual data > ntz
endfunction
//
//================================================================================
//
// other functions
//
//yg_bode(1) // plot yg (Glottal Volume Velocity)
frequency-phase response
//two_tubes_model_bode(1) // plot Two Tubes Model's
frequency-phase response
//three_tubes_model_bode(1) // plot Three Tubes Model's
frequency-phase response
//hpf_bode() // plot high pass filter's
frequency-phase response
//save_as_sound_file_yg( 'yg.wav' ) // save yg (Glottal Volume
Velocity) as one .wav file
//save_as_sound_file( 'y3out.wav' ) // save y3out (Sound
Pressure) as one .wav file
//plot_area(1) // plot sqrt(area) vs length
//plot_yg_yout() // plot yg (Glottal Volume Velocity) and y3out (Sound
Pressure)
//fft_plot( 1024 ) // FFT y3out(Sound Pressure) (1024
points) and plot frequency-phase
//
//===========================================================================================
//
// Add menu button of which name is 'functions'
//
//ADD_MENU=1; // set ADD_MENU 1 to
add menu button of some functions
//
//
//if ADD_MENU == 1 then
//delmenu('functions');
//if T_QTY == 4 then
//addmenu('functions',['three_tubes_model_bode(1)'; 'fft_plot(1024)';
'save_as_sound_file(''y3out.wav'')'; 'plot_area(1) '; 'plot_yg_yout()']
);
//functions=['three_tubes_model_bode(1)'; 'fft_plot(1024)';
'save_as_sound_file(''y3out.wav'')'; 'plot_area(1) '; 'plot_yg_yout()']
;
//elseif T_QTY == 3 then
//addmenu('functions',['three_tubes_model_bode(1)'; 'fft_plot(1024)';
'save_as_sound_file(''y3out.wav'')'; 'plot_area(1) '; 'plot_yg_yout()']
);
//functions=['three_tubes_model_bode(1)'; 'fft_plot(1024)';
'save_as_sound_file(''y3out.wav'')'; 'plot_area(1) '; 'plot_yg_yout()']
;
//else
//addmenu('functions',['two_tubes_model_bode(1)'; 'fft_plot(1024)';
'save_as_sound_file(''y3out.wav'')'; 'plot_area(1) '; 'plot_yg_yout()']
);
//functions=['two_tubes_model_bode(1)'; 'fft_plot(1024)';
'save_as_sound_file(''y3out.wav'')'; 'plot_area(1) '; 'plot_yg_yout()']
;
//end
//end //if ADD_MENU == 1 then/
//
//===========================================================================================
//
以上が サンプルプログラム TubeModel46.sci である。SCILABの古いバージョンであるがwindows用のscilab-
3.1.1
をつかって動作確認している。windows用のscilab- 4.1.2向けはこちら、また
は、 音をまとめて生成するサンプルプログラム。
注意事項。SCILABもバージョンによって仕様が違い上手く動かない箇所がある。例えば、さらに古いバージョンでは、波形を描
くためにつかって
いる plot
で、線の属性(実線とか破線とか、また、色など)を定義できないので、線の色などを別に定義するようにplotを変更し設定を追加する必要がある。
windows用のscilab-4.1.2では、波形を.wavでファイルに書き出す wavwrite
の仕様が変更(多チャンネル化対応?)されているため、このままだと、サウンドプレーヤーで再生できない。これを回避するためには、wavwrite
の引数の波形データの形式を 列 から 行 に変更する必要がある。 また、windows用のscilab-4.1.2では、矢印を描く
xarrows の矢印の大きさの定義もかわっている。そこで、断面積を描くなかで使用している
xarrows の矢印の大きさの数を大きく変更しないと、矢印ではなくただの横線になってしまう。
このサンプルプログラムは、2管の声道モデルのサンプルプログラムを3管に拡張したものであるので、
設定可能なパラメーターと補助的に使える関数の説明としては、こちらの2管声道モデルの
サンプルプログラムの内容を 参考にしていただきたい。
また、追加で拡張された設定可能なパラメーターの内容は
使用する声門モデルが、2管か3管かを選択する。管を直列に3個つないだ3管モデルを使用する場合、例えば「お」の場合はT_QTYを3
に、また、鼻音ように3つの管を Tの字につなぐ場合はT_QTYを4にする。
T_QTY=3; // T_QTY
defines which Tubes Model is used.
// set T_QTY 2 or other than below values when Two Tubes
Model
// set T_QTY 3 when Three Tubes Model of serial type
// set T_QTY 4 when Three Tubes Model of "T" type
管が3個になったので、第1管と第2管の分に追加して、更に、第3管の長さをL3に断面積をA3に、それぞれの区間の値を記入する。
// sample length & area for /o/ modoki
// set T_QTY=3 and use Three Tubes Model of serial type
L1=[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]; // set list of 1st
tube's length by unit is [cm]
A1=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]; // set list of
1st tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
L2=[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]; // set list of 2nd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
A2=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]; // set list of
2nd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
L3=[8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8]; // set list of 3rd
tube's length by unit is [cm]
A3=[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7]; // set list of
3rd tube's area by unit is [cm^2]
ボード線図などで描く周波数の上限の値。
Max_Freq=7500; // set plot maximum frequency by unit is [Hz]
3管をTの字につなぎあわせたときの(T_QTY = 4)、第3の管の先端の反射係数rl3。
完全に反射するときは -1 になる。
// reflection coefficient of 3rd tube's terminal side. 3rd tube is
supposed that one side is closed.
// This parameter is used only when T_QTY is set to 4 as Three
Tubes Model of "T" type
rl3=-0.97; // set certain a value, beside ideal value is -1
その他、追加で補助的につかえる関数は、
other functions
3個の管を直列につないだ3管モデルのボード線図(周波数と位相)を描く関数。
three_tubes_model_bode(1) // plot Three Tubes Model's
frequency-phase response
但し、3管モデルの伝達関数を求める計算は複雑なので(B5サイズのノートで2ページ分くらいの数式を計算する量
がある)間違っていたら
ごめんなさい。
声門の波形と
音圧の波形を描く。
plot_yg_yout() // plot yg (Glottal Volume Velocity) and y3out (Sound
Pressure)
音圧の波形の2番目の区間を開始としてポイント数のFFTを計算して、波形のボード線図(周波数と位相)を描く。(窓はHANNING)
fft_plot( 1024 ) // FFT y3out(Sound Pressure) (1024 points)
and plot frequency-phase
補
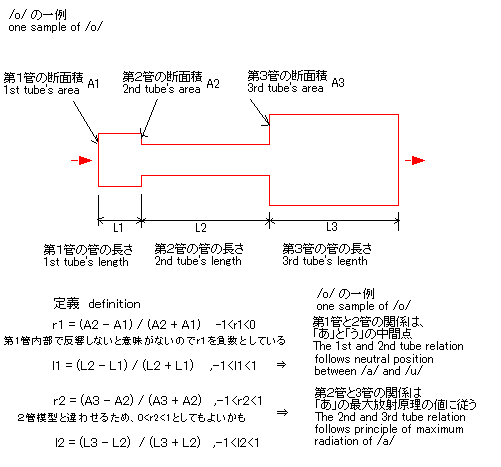
説:「お」(発音記号
/o/)の3管
(チューブ)模型における位置
下図の様に、「お」の3管模型上の位置は、第2管と3管は「あ」に似た口からの放射効率が最大になる付近で、第1管と2管の位置は、「あ」と見なされると
ころと 「う」と見なされるところ の間の中間点にあると考えられる。
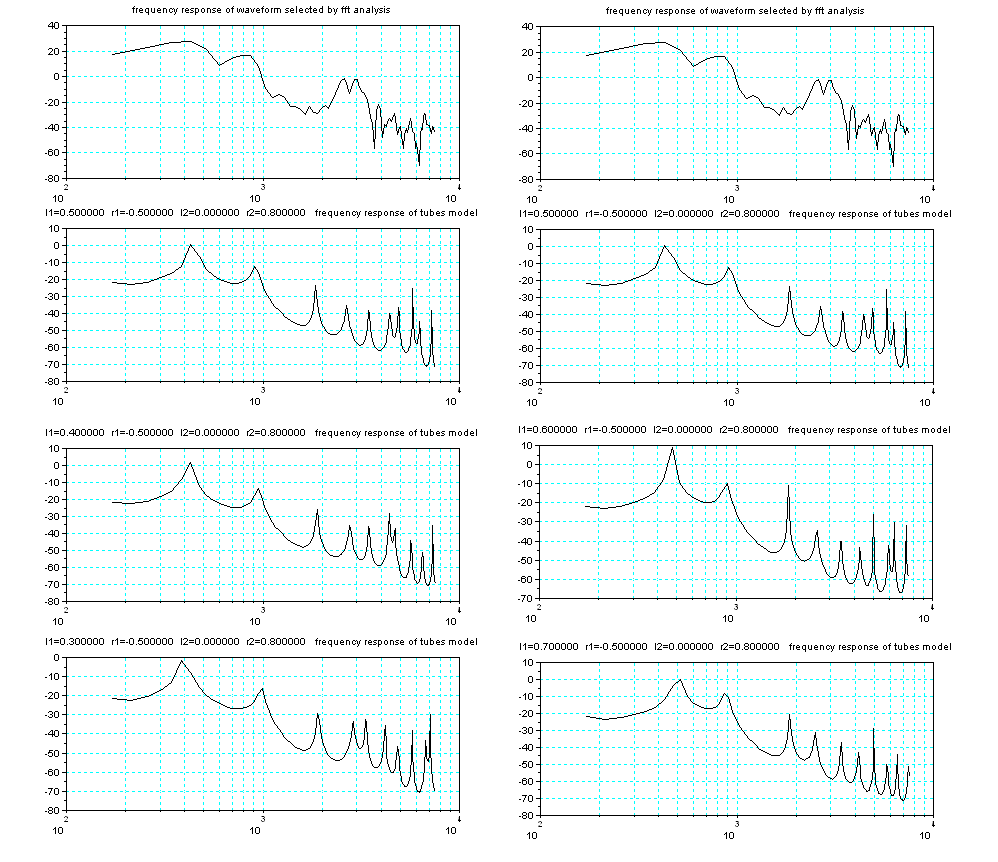
他の値は固定して、l1だけを変化させたときの、理論スペクトルの変化は下図のようになる。
l1が 0.5 0.4
0.3 と変化するにつれて、ピークの山の間隔が広がり等分に近くなり、より「う」の音になる(下図左側
上から下)。 また、 l1が
0.5 0.6
0.7 と変化するにつれて、ピークの山の間隔が狭くなり、より「あ」の音に近づいていく(下図右側 上
から下)。 「お」は、丁度、中間点に位置している。
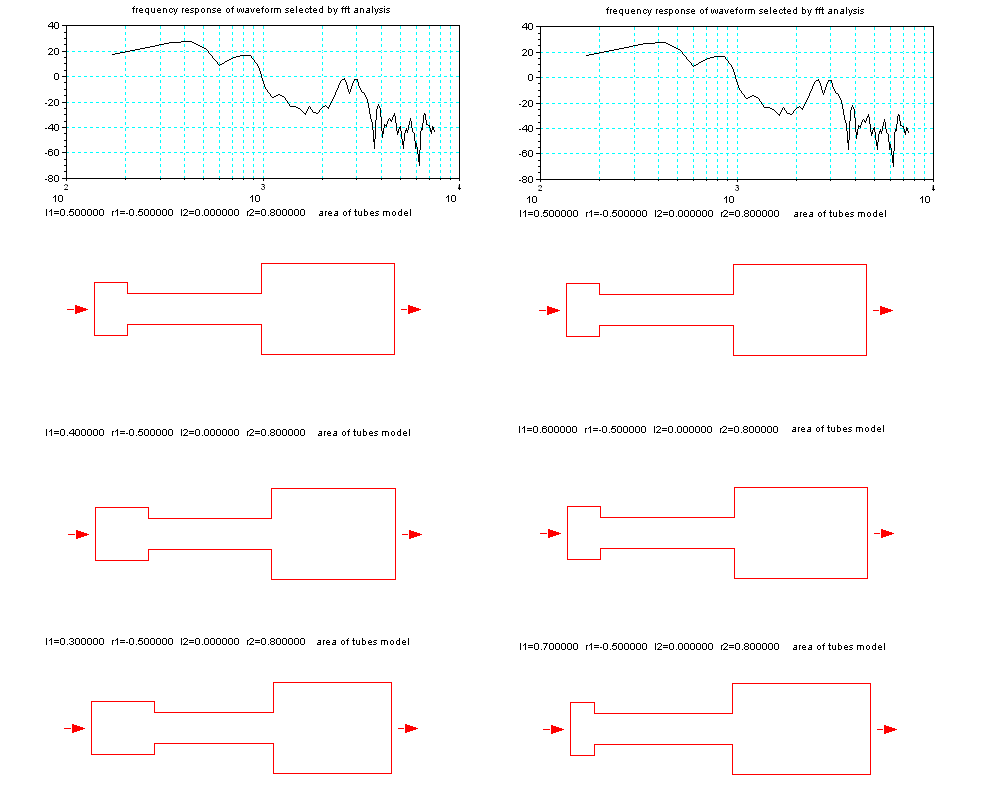
同じことを断面積の変化でみると下図のようになる。
No.9b 2009年7月4日